Serum dilution
110 likes | 347 Vues
A. B. CP5. PNAG. OD 405 nm. OD 405 nm. Serum dilution. Serum dilution. C. CP8.

Serum dilution
E N D
Presentation Transcript
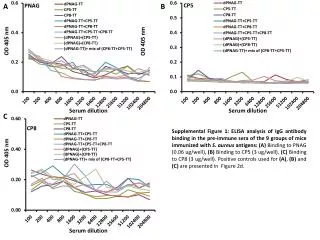
A B CP5 PNAG OD 405 nm OD 405 nm Serum dilution Serum dilution C CP8 Supplemental Figure 1: ELISA analysis of IgG antibody binding in the pre-immune sera of the 9 groups of mice immunized with S. aureus antigens:(A) Binding toPNAG (0.06 ug/well), (B) Binding to CP5 (3 ug/well), (C) Binding to CP8 (3 ug/well). Positive controls used for (A), (B) and (C) are presented in Figure 2d. OD 405 nm Serum dilution
A B CP5 PNAG OD 405 nm OD 405 nm Serum dilution Serum dilution C D CP8 PNAG OD 405 nm OD 405 nm CP5 OD 405 nm CP8 OD 405 nm Serum dilution Serum dilution Supplemental Figure 2: IgG responses to S. aureus antigens following immunization A. Binding to PNAG (0.06 ug/well). B. Binding to CP5 (3 ug/well), (C) Binding to CP8 (3 ug/well). Mice immunized with the indicated antigens. Dashed lines: no immune response to PNAG, CP5 or CP8 detected in sera from mice injected with vaccines not containing these antigens. D: Top, center and bottom: positive controls used for (A): Rabbit polyclonal antibodies to PNAG, (B): Mouse monoclonal antibodies to CP5 and (C): Rabbit polyclonal antibodies to CP8.
A Supplemental Figure 3A: Killing of S. aureus Newman (CP5) at the indicated concentrationin antisera from mice immunized with combinations of dPNAG-TT, CP5-TT and CP8-TT administrated together or separately into different flanks but at the same time. No killing >30% was detected in any antiserum. Controls: Pre-immune sera. Pre-immune sera Serum dilutions Percent S. aureus Newman killed (dPNAG-TT + CP5-TT) (dPNAG-TT + CP5-TT + CP8-TT) (dPNAG-TT) + (CP5-TT) (dPNAG-TT + CP8-TT) (dPNAG-TT) + (CP8-TT) (dPNAG-TT) + (CP5-TT + CP8-TT) 10 40 160 Combinations of antigens given together Combinations of antigens given separately 10 40 160 10 40 160 10 40 160 10 40 160 10 40 160
B Supplemental Figure 3B: Killing of S. aureus PS80 (CP8) at the indicated concentrationin antisera from mice immunized with combinations of dPNAG-TT, CP5-TT and CP8-TT administrated together or separately into different flanks but at the same time. No killing >30% was detected in any antiserum. Controls: Pre-immune sera. Pre-immune sera Serum dilutions Percent S. aureus Newman killed (dPNAG-TT) + (CP5-TT) (dPNAG-TT) + (CP8-TT) (dPNAG-TT + CP5-TT + CP8-TT) (dPNAG-TT) + (CP5-TT + CP8-TT) (dPNAG-TT + CP5-TT) (dPNAG-TT + CP8-TT) 10 40 160 Combinations of antigens given together Combinations of antigens given separately 10 40 160 10 40 160 10 40 160 10 40 160 10 40 160
Supplemental Figure 3C: Killing of S. aureus LAC (Non-typable) by sera from mice immunized with the indicated antigens. Only antibody to dPNAG-TT mediated killing >30%. Control: Pre-immune serum. Pre-immune sera Immune sera Percent S. aureus LAC killed dPNAG-TT (dPNAG-TT+ CP-TT5 + CP8-TT) Control (dPNAG-TT) + (CP5-TT) CP5-TT (dPNAG) + (CP8-TT) (dPNAG-TT+ CP5-TT) (dPNAG-TT+ CP8-TT) (dPNAG-TT) + (CP5-TT+CP8-TT) CP8-TT Combinations of antigens given together Combinations of antigens given separately Antigens administrated alone
A B S. aureus MN8 mutants used for the absorption S. aureus Newman mutants used for absorption Percent S. aureusNewman killed Percent S. aureusPS80 killed Dica+Dcap Dica+Dcap Dica Dica Dcap Dcap Serum dilution Serum dilution C D Percent S. aureusPS80 killed Percent S. aureusNewman killed S. aureusNewman mutants used for the absorption S. aureus MN8 mutants used for the absorption Dica+Dcap Dica+Dcap Dcap Dcap Serum dilution Serum dilution Supplemental Figure 4: OPKA after specific absorptions of the sera from the mice immunized with combinations of antigen injected together. Killing of S. aureus Newman (CP5) (A and C) or PS80 (CP8) (B and D) in antisera of mice immunized with dPNAG-TT+ CP5-TT (A) , dPNAG-TT+CP8-TT (B), or dPNAG-TT+CP5-TT+CP8-TT (C-D), after absorption with S. aureus double mutants(Dcap+Dica) to leave behind antibodies to both PNAG and CP or with individual Dica or Dcap mutants to leave behind only antibodies to PNAG or to CP, respectively. Bars indicate average of 4 replicates per assay. Control: No complement in assay tube.
A B S. aureus MN8 mutants used for the absorption S. aureusNewman mutants used for the absorption Percent S. aureusNewman killed Percent S. aureusPS80 killed Dica+Dcap Dica Dica+Dcap Dcap Dica Dcap Serum dilution Serum dilution C D Percent S. aureusPS80 killed Percent S. aureusNewman killed S. aureus MN8 mutants used for the absorption S. aureusNewman mutants used for the absorption Dica+Dcap Dica+Dcap Dcap Dcap Serum dilution Serum dilution Supplemental Figure 5: OPKA after absorption of antisera from the mice immunized with combinations of antigens injected into separate flanks. Killing of S. aureus Newman (CP5) (A and C) or PS80 (CP8) (B and D) in antisera from mice immunized with dPNAG-TT & CP5-TT (A); , dPNAG-TT & CP8-TT (B); or dPNAG-TT & CP5-TT+CP8-TT (C-D); injected separately after absorption with S. aureus double mutant(Dcap+Dica) to leave behind antibodies to both PNAG and CP or with individual Dica or Dcap mutants to leave behind only antibodies to PNAG or CP, respectively. Bars indicate average of 4 replicates per assay. Controls: No complement.
A B Anti-dPNAG-TT + absorbed NHS (Dica) Anti-dPNAG-TT + absorbed NHS (Dcap) Anti-dPNAG-TT + Unabsorbed NHS Anti-dPNAG-TT + Unabsorbed NHS Anti-dPNAG-TT + absorbed NHS (Dica) Anti-dPNAG-TT + absorbed NHS (Dcap) Percent S. aureusNewman killed Percent S. aureusPS80 killed 10 40 160 10 40 160 10 40 160 10 40 160 10 40 160 10 40 160 Serum dilution Serum dilution Supplemental Figure 6: Effect of addition of pooled normal human sera on OPK of rabbit antisera raised to dPNAG-TT: OPK of S. aureus Newman (A) or PS80 (B) mediated by rabbit antibody to dPNAG-TT and effect of the addition of pooled NHS, either unabsorbed or absorbed with S. aureus mutants to leave behind only antibodies to PNAG (S. aureus Dica) or antibodies to CP (S. aureus Dcap). Bars indicate average of 4 replicates per assay. Controls lacking complement had a killing <1%.
A Rabbit anti-CP5-TT + NHS absorbed (Dcap) Rabbit anti-CP5-TT +Unabsorbed NHS Rabbit anti-CP5-TT Percent S. aureusNewman killed NHS B Serum dilution P<0.01 Supplemental Figure 7: Characteristics of a pool of NHS prepared from individual NHS. Pool prepared from sera with high levels of interference with the OPK of rabbit antibody to CP5-TT. A. OPKA against S. aureus Newman in rabbit antisera raised to CP5-TT , the selected NHS pool and a 1:10 dilution of the rabbit antisera added to indicated dilutions of the NHS, either unabsorbed or absorbed with S. aureus Dcap to remove the antibodies to PNAG. NRS=Normal rabbit serum, No C’=No complement, No PMN=No Polymorphonuclear leukocytes. B. Effect of the NHS pool on reduction in the cfuS. aureus/abscess mediated by rabbit antibody to CP5-TT. Antibody raised to CP5-TT without added NHS significantly reduced the cfuS. aureus/abscess compared with mice injected with antibody raised to CP5-TT into which NHS had been added or mice injected with NHS alone. Overall ANOVA P =0.006, pair-wise comparisons on figures. Challenge: S. aureus Newman (106cfu). P<0.05 NS Anti-CP5-TT NHS Anti-CP5-TT + NHS
B A Rabbit anti-CP5-TT + NHS adsorbed with E. coli. Rabbit anti-CP5-TT Rabbit anti-CP8-TT + NHS adsorbed with E. coli. Rabbit anti-CP8-TT Rabbit anti-CP5-TT +NHS adsorbed with E. coli Dpga Rabbit anti-CP8-TT +NHS adsorbed with E. coli Dpga Percent of S. aureus Newman killed Percent of S. aureus PS80 killed Supplemental Figure 8: Effect on the OPK activity mediated by anti-capsule antibodies of a pool of NHS with and without absorbtion of the anti-PNAG antibodies by E. coli, a non-S. aureus PNAG-producing bacteria. A. OPKA against S. aureus Newman in rabbit antisera raised to CP5-TT, a 1:10 dilution of the rabbit antisera added to indicated dilutions of the NHS, either absorbed with E. coli Jto remove the antibodies to PNAG or E. coli J Dpga to leave behind antibodies to PNAG. NHS=Normal Human Serum, No C’=No complement. B. OPKA against S. aureus PS80 in rabbit antisera raised to CP8-TT, a 1:10 dilution of the rabbit antisera added to indicated dilutions of the NHS, either absorbed with E. coli Jto remove the antibodies to PNAG or E. coli J Dpga to leave behind antibodies to PNAG. NHS=Normal Human Serum, No C’=No complement. Pool prepared from sera with high levels of interference with the OPK of rabbit antibodies to CP5-TT and CP8-TT.
A B P<0.05 P<0.05 P<0.05 P<0.05 NS NS Supplemental Figure 9 : Effect of pooled NHS on the CFU of S. aureus/ml of blooddetected in mice passively administered rabbit antibodies to CP5-TT or CP8-TT. A: CFU S. aureus Newman/ml of blood in mice injected with rabbit antibodies to CP5-TT, CP5-TT plus NHS or NHS alone. Overall ANOVA, P<0.0001, Dunnett’s post-hoc test pair-wise comparisons shown on figure. Challenge: S. aureus Newman (2.0x107cfu). B: CFU S. aureus PS80/ml of blood in mice injected with rabbit antibodies to CP8-TT, CP8-TT plus NHS or NHS alone. Overall ANOVA P<0.0001, Dunnett’s post-hoc test pair-wise comparisons shown on figure. Challenge: S. aureus PS80 (5.3x107 cfu). NS-not significant.