Normal Blood Cell Morphology
160 likes | 337 Vues
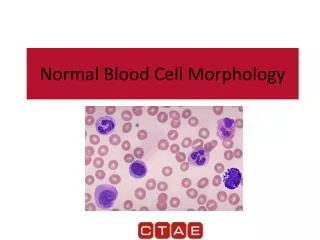
Normal Blood Cell Morphology. Types of White Blood Cells. White blood cells AKA: Leukocytes or WBCs Largest sized blood cells Lowest numbers in the blood (4,500 – 11,000 per microliter) Formed in the bone marrow and some in the lymph glands Primary cells of the immune system

Normal Blood Cell Morphology
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Types of White Blood Cells • White blood cells • AKA: Leukocytes or WBCs • Largest sized blood cells • Lowest numbers in the blood (4,500 – 11,000 per microliter) • Formed in the bone marrow and some in the lymph glands • Primary cells of the immune system • Fights disease and foreign invaders http://www.giantmicrobes.com/us/products/whitebloodcell.html
Types of White Blood Cells • White blood cells • Contain nuclei with DNA, the shape depends on the type of cell • Certain WBCs produce antibodies • Life span is from 24 hours to several years • Size is 8-20 micrometers • There are five different types of WBCs • Neutrophils • Eosinophils • Basophils • Lymphocytes • Monocytes http://www.giantmicrobes.com/us/products/whitebloodcell.html
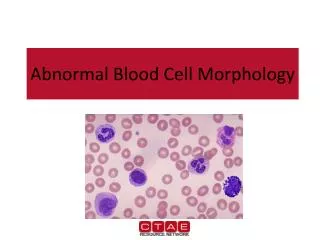
Types of White Blood Cells • Leukocytes can be divided into two groups. • Granulocytes • Contain granules; inclusions in their cytoplasm • Usually have lobulated or segmented nuclei • Neutrophils • Basophils • Eosinophils • Agranulocytes • Do not contain granules • Do not have lobulated or segmented nuclei • Monocytes • Lymphocytes
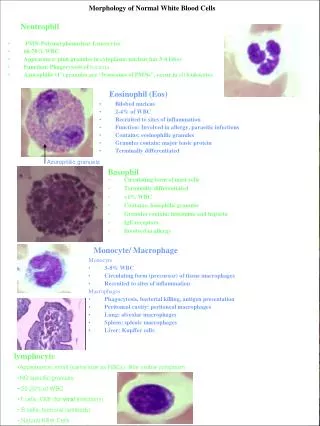
Types of White Blood Cells • Neutrophils (AKA: PMNs, Polys, Segs) • Account for the highest amount of WBCs [~60%] • Fight off bacterial invaders • Fight off fungal invaders • Take part in phagocytosis • Neutrophils look like….. • Nucleus is divided into 2 to 5 segments and stains dark purple (multi-lobed nucleus) • Cytoplasm is pale pink to tan with fine pink-purple granules • 10-15 micrometers in diameter • Mature form = segmented (segs); Nucleus has 2-5 lobes • Immature form = band (bands); no segments in nucleus • Bands are normal in the peripheral blood in low numbers 0-5% • When did you see them? • High numbers during bacterial infections and inflammation
Types of White Blood Cells • Eosinophils (AKA: Eos) • Fight off parasitic worm and flukes • Important in allergic reactions • ~ 3 % of WBCs in the blood • Eosinophils look like….. • Nucleus is divided into 2 segments • Cytoplasm is pale pink to tan with large orange and red granules • 10-15 micrometers in diameter • When did you see them? • High numbers with parasitic infections • Higher numbers in allergic reactions
Types of White Blood Cells • Basophils • Releases histamine in response to an allergic reaction • Seen with inflammation • Lowest number of WBCs in blood [<1%] • Basophils look like….. • Nucleus has 2 lobes that stains purple and is difficult to see • Cytoplasm is pale pink –tan but contains large purple/blue-black granules • 10-15 micrometers in diameter • When did you see them? • High numbers during allergic reactions • High numbers during inflammatory reactions
Types of White Blood Cells • Monocyte • Search for bacteria and viruses • Participate in phagocytosis • Largest of the white blood cells • ~ 6 % of WBCs in the blood • Monocytes look like….. • Singular nucleus (convoluted shape); kidney shaped, bean shaped, or horseshoe shaped with a deep indentation • Stains a blue-gray color with “ground glass” cytoplasm, tiny granules • Vacuoles are sometimes present • 12-20 micrometers in diameter • When did you see them? • High numbers during bacterial and viral infections
Types of White Blood Cells • Lymphocyte • Fight viral infections • Some produce and secrete antibodies • 2nd most common WBC in blood • ~ 30 % of WBCs in the blood • Lymphocytes look like….. • Large, dark staining nucleus, round or oval • Little to no cytoplasm, blue in color • Occasional purple-reddish granules • About the size of a RBC • 8-15 micrometers in diameter • Smallest nucleated cell in peripheral circulation • When did you see them? • High numbers during viral infections • High and atypical form during infectious mononucleosis
Platelets • Platelets (AKA: Thrombocytes or PLTs) • Formed from the fragments of a megakaryocyte • Not considered a WBC • Function in hemostasis • Platelets are found in the peripheral blood • Megakaryocytes are found in the bone marrow • Platelets look like….. • Small about 2-3 micrometers in diameter • Fragments • Stains bluish and usually contains small reddish-purple granules • Oval or round but can have spiny projections • Normal is between 7-20 per field
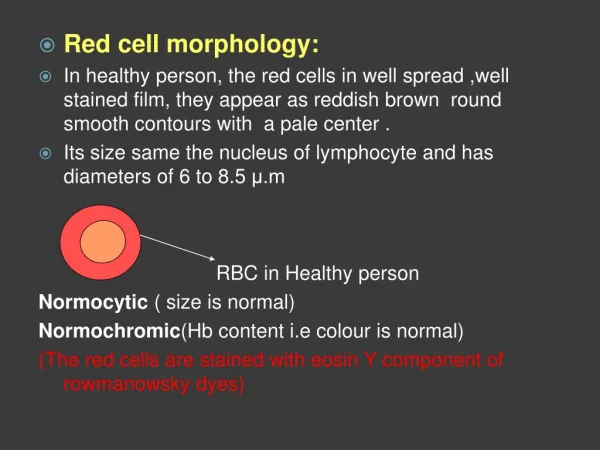
Red Blood Cells • Red Blood Cells (AKA: Erythrocytes of RBCs) • Normal sized (oval or round) = called normocytic • If the RBC color is normal = called normochromic