Energy Transfer in Ecosystems
120 likes | 193 Vues
Learn about how producers convert energy for ecosystem use, the role of consumers, energy flow, trophic levels, and the significance of food chains and webs. Explore the dynamics of biomass, energy pyramids, and the interconnectedness of organisms in an ecosystem.

Energy Transfer in Ecosystems
E N D
Presentation Transcript
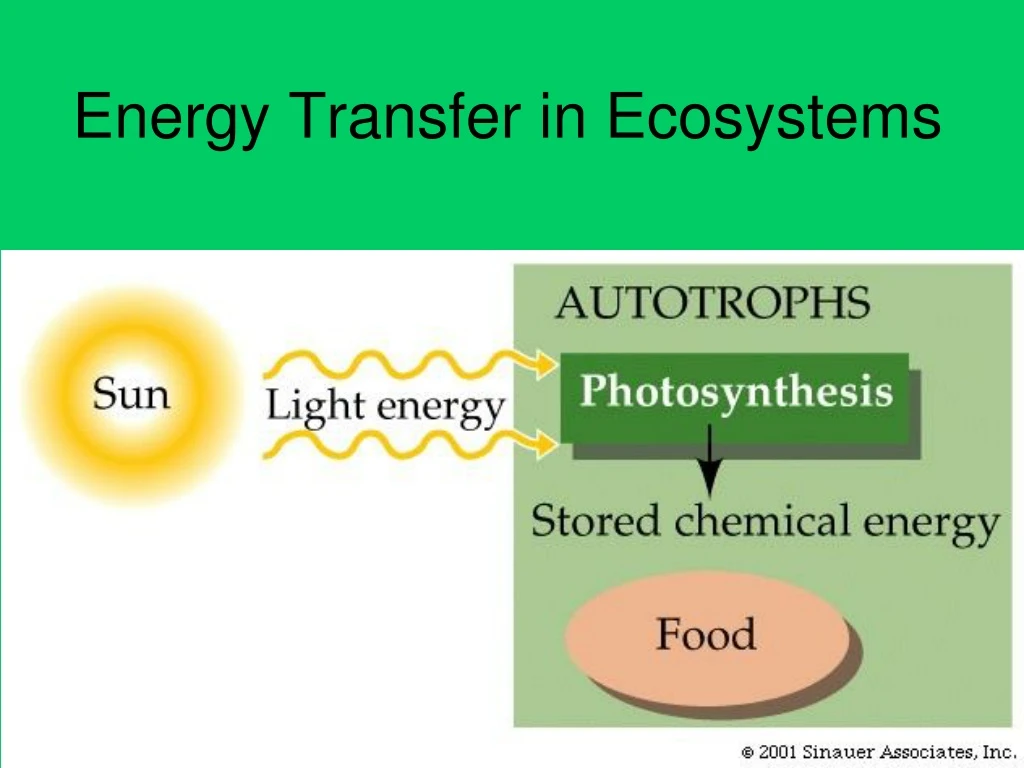
Producers… • Are autotrophs that convert energy entering the ecosystem so other organisms can use it • Ex. Plants, protists, bacteria, algae • Most use solar energy to do photosynthesis some use inorganic molecules to do chemosynthesis • Producers add biomass to an ecosystem • Biomass is all of the organic material in an ecosystem available to organisms
An ecosystem is… • All of the biotic and abiotic components of an area • The amount of energy an ecosystem receives has an effect on its makeup • All energy entering the ecosystem from the sun or other abiotic factors needs to be converted to be useful to other organisms
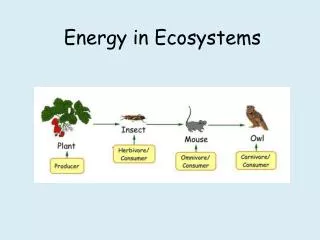
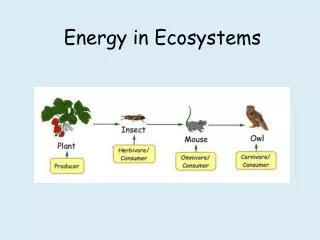
Amount of producers will affect the types of consumers present in the ecosystem • Consumers are heterotrophs that must eat other organisms for nutrition • Consumers are grouped according to their food consumption: • Herbivores eat producers • Carnivores eat other consumers • Omnivores eat both producers and consumers • Detritivores eat wastes and parts of dead consumers and producers. Some detritivores are decomposers • Decomposers are bacteria and fungi that decay any living material
What kind of consumer? HERBIVORE DECOMPOSER CARNIVORE OMNIVORE HERBIVORE
All ecosystems have energy flow caused by organisms eating one another • Energy flows through ecosystems from producers to consumers • Energy flow can be diagrammed in many ways including: • Ecological Pyramids • Trophic Level Diagrams • Energy Pyramids • Food chains • Food webs
Trophic level diagrams • An organism’s trophic level shows their position in the sequence of energy flow • Producers belong to the 1st trophic level (are most abundant) • Herbivores belong to the 2nd trophic level (also called primary consumers) • Predators of herbivores belong to the 3rd trophic level (also called secondary consumers) • Most ecosystems only have 3 or 4 trophic levels
Type of Consumer Trophic Level • Secondary Consumer • Primary Consumer • Producer • 3 • 2 • 1
Energy Pyramids • Energy pyramids show how much energy is passed from one trophic level to the next • On average 10% of all energy consumed can be passed on to the next trophic level, but it can be as low as 1% or as high as 20% • Most energy consumed contributes to maintaining homeostasis, respiration, growth, and reproduction
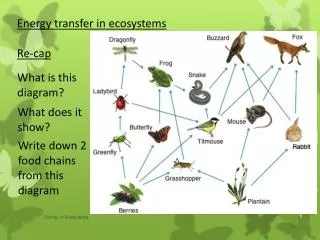
Food Chains • Food chains are single pathways of energy transfer. • The arrows represent the way the energy is flowing. • So the energy is flowing from the frog to the snake in this food chain • Food chains are too simple to encompass a whole ecosystems interactions
Food webs • Food webs are made of many interacting food chains. • More accurate than food chains since most organisms feed on more than one thing and are eaten by more than one thing • If one part of the food web in lost there can be serious consequences for the entire ecosystem