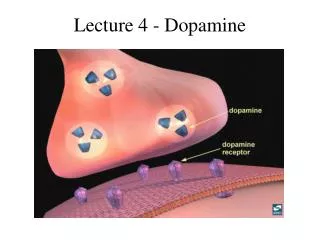
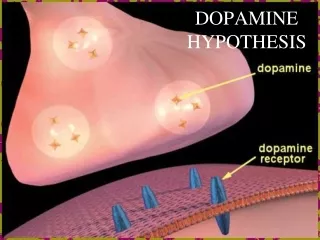
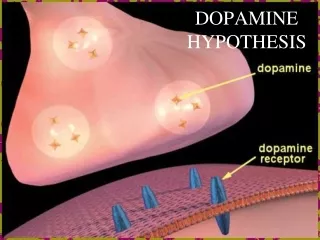
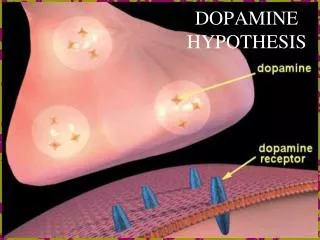
Dopamine (DA) neuron
440 likes | 631 Vues
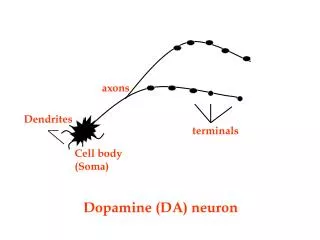
axons. Dendrites. terminals. Cell body (Soma). Dopamine (DA) neuron. Most information comes in here. axons. Dendrites. terminals. Cell body (Soma). Dopamine (DA) neuron. Chemical signals Generate EPSPs Or IPSPs. axons. terminals. Cell body (Soma). Dopamine (DA) neuron.

Dopamine (DA) neuron
E N D
Presentation Transcript
axons Dendrites terminals Cell body (Soma) Dopamine (DA) neuron
Most information comes in here axons Dendrites terminals Cell body (Soma) Dopamine (DA) neuron
Chemical signals Generate EPSPs Or IPSPs axons terminals Cell body (Soma) Dopamine (DA) neuron
If excitation caused By EPSPs is great Enough to cross the threshold, An Action Potenial is generated. axons terminals Cell body (point of origin) Dopamine (DA) neuron
Action Potentials travel along the axon axons terminals Cell body (point of origin) Dopamine (DA) neuron
Action Potentials travel along the axon axons terminals Cell body (point of origin) Dopamine (DA) neuron
AXON Towards terminals Towards soma
Excitation above the threshold Opens Voltage-gated Na+ channels Na+ AXON Towards terminals Towards soma
Na+ ions rush into cell, causing Action Potential (ascending part) Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ AXON Towards terminals Towards soma
Action Potential is propagated down The Axon K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ K+ moves out To restore resting Potential (i.e., Descending part) AXON Towards terminals Towards soma
Action Potential is propagated down The Axon K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ AXON Towards terminals Towards soma
Action Potential is propagated down The Axon K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ AXON Towards terminals Towards soma
Action Potential is propagated down The Axon K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ AXON Towards terminals Towards soma
Action Potential is propagated down The Axon K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ AXON Towards terminals Towards soma
Action Potential is propagated down The Axon K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ AXON Towards terminals Towards soma
Action Potential is propagated down The Axon K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ AXON Towards terminals Towards soma
Action Potential is propagated down The Axon K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ AXON Towards terminals Towards soma
Action Potential is propagated down The Axon K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ AXON Towards terminals Towards soma
Action Potential is propagated down The Axon K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ AXON Towards terminals Towards soma
Action Potential is propagated down The Axon K+ Na+ Na+ Na+ Na+ K+ AXON Towards terminals Towards soma
Action Potentials travel along the axon axons terminals Cell body (point of origin) Dopamine (DA) neuron
axons terminals Cell body (point of origin) Dopamine (DA) neuron
axons terminals Cell body (point of origin) Dopamine (DA) neuron
axons terminals Cell body (point of origin) Dopamine (DA) neuron
axons terminals Cell body (point of origin) Dopamine (DA) neuron
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . axons . . . . . . . . . causing neurotransmitter release from the terminals Cell body (point of origin) Dopamine (DA) neuron
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . axons . . . . . . . . causing neurotransmitter release from the terminals Cell body (point of origin) Dopamine (DA) neuron
SYNAPSE: Point of functional connection DA terminal Transmitter is stored In vesicles Synaptic cleft Postsynaptic cell
Electrical impulse “action potential” DA terminal Synaptic cleft Postsynaptic cell
DA terminal Synaptic cleft Postsynaptic cell
DA terminal Ca++ Synaptic cleft Postsynaptic cell
DA terminal Ca++ Ca++ Ca++ Ca++ Synaptic cleft Postsynaptic cell
DA terminal . . . . . Transmitter is released Synaptic cleft Postsynaptic cell
DA terminal . Transmitter diffuses across synaptic cleft . . . . Synaptic cleft . Postsynaptic cell
DA terminal Transmitter diffuses across synaptic cleft Synaptic cleft . . . . . . Postsynaptic cell
DA terminal Transmitter binds to postsynaptic receptors Synaptic cleft . . . . . . DA Receptor proteins Postsynaptic cell
DA terminal Synaptic cleft Physiological and biochemical effects (EPSPs or IPSPs) Postsynaptic cell
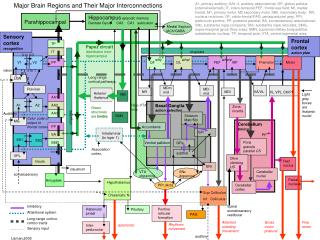
STUDIES OF THE BEHAVIORAL EFFECTS OF DRUGS DRUGS MODIFY THE PROCESS OF CHEMICAL TRANSMISSION IN THE NERVOUS SYSTEM • Alter neurotransmitter synthesis • Block storage of transmitter • Stimulate or reduce release • Stimulate or block receptors • Block the inactivation (enzymatic breakdown or uptake) of transmitter
PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS • Prozac • Zoloft BLOCK THE INACTIVATION OF SEROTONIN (5-HT) - other antidepressants can have actions on other transmitters (NE)
PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY ANTIPSYCHOTIC DRUGS • Haldol • Thorazine • Clozapine BLOCK RECEPTORS FOR THE NEUROTRANSMITTER DOPAMINE (DA)
PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY ANTIANXIETY DRUGS • Valium • Librium • Xanax FACILITATE THE INHIBITORY ACTIONS OF GABA ON A TYPE OF GABA RECEPTOR (GABAA)
PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY STIMULANT DRUGS • Cocaine • Methamphetamine • Ritalin BLOCK THE INACTIVATION OF DOPAMINE (DA), or STIMULATE RELEASE OF DA; also act on NE and 5-HT
PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY MINOR STIMULANT DRUGS • Caffeine • Theophylline • (components of coffee, tea, “energy” drinks) BLOCK ADENOSINE RECEPTORS







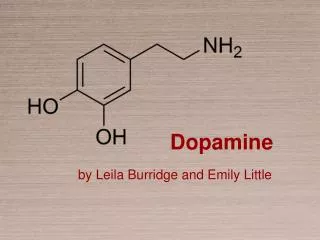

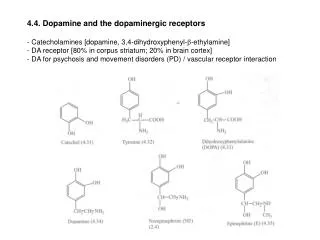
![Catecholamines (dopamine [DA], norepinephrine [NE], epinephrine [EPI])](https://cdn2.slideserve.com/3865027/catecholamines-dopamine-da-norepinephrine-ne-epinephrine-epi-dt.jpg)