a -syn
10 likes | 155 Vues
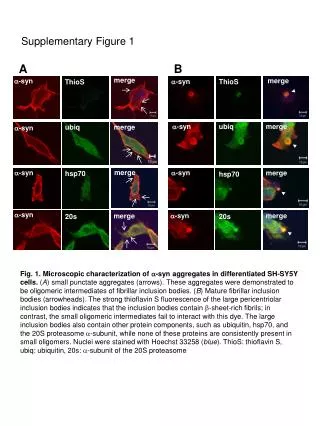
Supplementary Figure 1. A. B. merge. merge. a -syn. a -syn. ThioS. ThioS. a -syn. ubiq. merge. ubiq. merge. a -syn. merge. a -syn. a -syn. merge. hsp70. hsp70. a -syn. a -syn. merge. merge. 20s. 20s.

a -syn
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Supplementary Figure 1 A B merge merge a-syn a-syn ThioS ThioS a-syn ubiq merge ubiq merge a-syn merge a-syn a-syn merge hsp70 hsp70 a-syn a-syn merge merge 20s 20s Fig. 1.Microscopic characterization of a-syn aggregates in differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. (A) small punctate aggregates (arrows). These aggregates were demonstrated to be oligomeric intermediates of fibrillar inclusion bodies. (B) Mature fibrillar inclusion bodies (arrowheads). The strong thioflavin S fluorescence of the large pericentriolar inclusion bodies indicates that the inclusion bodies contain b-sheet-rich fibrils; in contrast, the small oligomeric intermediates fail to interact with this dye. The large inclusion bodies also contain other protein components, such as ubiquitin, hsp70, and the 20S proteasome a-subunit, while none of these proteins are consistently present in small oligomers. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258 (blue). ThioS: thioflavin S, ubiq: ubiquitin, 20s: a-subunit of the 20S proteasome