Analyzing Forces and Momentum in a 10 kg Box
210 likes | 357 Vues
This exercise explores the dynamics of a 10 kg box sliding on a level floor under the influence of friction. Participants will create a force diagram to assess the box's weight, calculate the friction force using a kinetic friction coefficient of 0.5, and determine the box's acceleration. Additionally, the implications of increasing the box's mass to 20 kg will be analyzed. The task enhances understanding of Newton's laws, momentum, and impulse, crucial for grasping fundamental physics concepts.

Analyzing Forces and Momentum in a 10 kg Box
E N D
Presentation Transcript
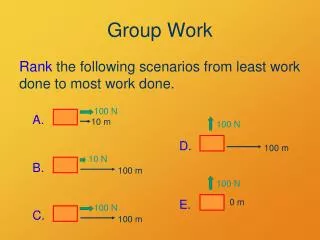
Group Work A 10-kg box slides on a level floor. Make a force diagram for it. What is its weight? Its coefficient of kinetic (sliding) friction against the floor is mk = 0.5. What is the force of friction between box and floor? What is the acceleration of the box? What would the answer to d be if the box’s mass were 20 kg?
Announcements • Exam 1 on Moodle today • Opened 6 AM • Closes midnight • 1.5-hour time limit • Open-note, open-book, etc. • No consultation or collaboration permitted
Momentum the quantity of motion
Objectives • Define momentum. • Define impulse and describe its relationship to momentum.
What’s the point? • Nature keeps careful account of momentum.
Think Question Which process requires more time? • Pulling as hard as you can to accelerate a little red wagon from rest to a speed of 1 m/s. • Pulling as hard as you can to accelerate a horse trailer from rest to a speed of 1 m/s. • The two take the same amount of time.
Think Question Which process requires more force? • Accelerating a little red wagon from rest to a speed of 1m/s in ten seconds. • Accelerating a horse trailer from rest to a speed of 1m/s in ten seconds. • The two take the same force.
Dv = FDt m Example Problem Show that when a constant net force F is applied to an object of mass m for a time Dt, its change in velocity is Strategy: We can find acceleration using Newton’s second law a = F/m. Then we can find Dv using the definition of acceleration a = Dv/Dt.
m F Dt Dv 1 kg 10 N 1 s 1 kg 10 N 10 s 1 kg 1 N 10 s 10 kg 10 N 10 s Group Work • From mass m, net force F, and duration Dt, find acceleration a and velocity change Dv. a J Dp
Impulse = FDt where F Is net force Dt is duration Impulse Impulse is a vector.
Think Question Two objects of different masses move at the same speed. Which one is harder to stop? The lighter object. The more massive object.
Think Question Two objects with the same mass move at different speeds. Which one is harder to stop? The faster object. The slower object.
p = mv Momentum Formula momentum is a vector.
Think Question Two spaceships have the same velocity, with one’s mass twice the other’s. The heavy one’s momentum is: • more than twice the light one’s momentum. • twice the light one’s momentum. • the same as the light one’s momentum. • half the light one’s momentum. • less than half the light one’s momentum.
Think Question Two spaceships have the same mass, but one’s speed is twice the other’s. The faster one’s momentum is: • more than twice the slower one’s momentum. • twice the slower one’s momentum. • the same as the slower one’s momentum. • half the slower one’s momentum. • less than half the slower one’s momentum.
m F Dt J Dp Group Work • From m, F, Dt, Dv, find impulse J and momentum change Dp. 1 kg 10 N 1 s 1 kg 10 N 10 s 1 kg 1 N 10 s 10 kg 10 N 10 s
Group Work • Show that when a net force F is applied to an object of mass m for a time Dt, its change in momentum is Dp = FDt Hint: You can find its momentum change from its mass and its velocity change.
Impulse-Momentum Theorem • Impulse = FDt. • FDt = maDt = mDv = D(mv) = Dp • So impulse = change in momentum
Poll Question Which changes its momentum the most? • A moving object that stops when it hits a barrier. • A moving object that bounces back from a barrier. Hints: How is Dp defined? Momentum is a vector.Which receives the greater impulse?
final p – initial p final p – initial p initial p initial p Dp Dp final p final p= 0 Rebound and Momentum
Reading for Next Time Newton’s third law Conservation of momentum Big ideas: Forces are always between objects Objects trade momentum when they interact