Feedback Dynamics and Feedback Loop
350 likes | 1.27k Vues
Feedback Dynamics and Feedback Loop. Dr. Manish Semwal GMIS. System. A system is a set of dynamic, interacting elements, organized for a process of achievement. Closed System.

Feedback Dynamics and Feedback Loop
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Feedback Dynamics and Feedback Loop Dr. Manish Semwal GMIS
System • A system is a set of dynamic, interacting elements, organized for a process of achievement.
Closed System • A closed system is one that is isolated from its environment. This kind of system uses its own internal reserve of potential energy, and as reactions take place, entropy rises irreversibly to a maximum. Thermodynamic equilibrium is reached, and the system can no longer produce work.
Open System • An open system is one in permanent interaction with its environment, with which it exchanges energy, matter and information. Because of the energy flow through the system and the dumping of “used” energy into the environment, its entropy is maintained at a relatively low level. Thissystemis capable of performing work.
Feedback • feedback is a process whereby some proportion or in general, function, of the output signal of a system is passed (fed back) to the input. Often this is done intentionally, in order to control the dynamic behaviour of the system. Feedback is observed or used in various areas dealing with complex systems,
Feedback Loop • the complete causal path that leads from the initial detection of the gap to the subsequent modification of the gap. • Feedback Loops can enhance or buffer changes that occur in a system.
Positive Feedback • Positive feedback loop = instead of stabilizing a system, it drives it further toward one extreme or another • Exponential growth in human population, erosion, melting sea ice • Rare in nature • But is common in natural systems altered by humans
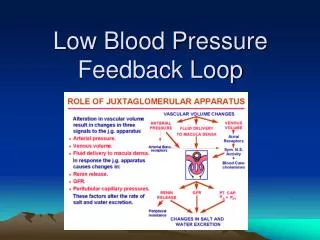
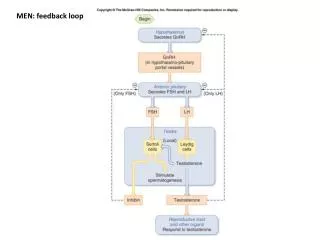
Negative Feedback • Negative feedback loops represent control and stability, the establishment of equilibrium and self-maintenance.
Room temp increases Set point is reached Set point is reached Room temp is below the setpoint Room temp is above the setpoint Room temp decreases Heater turns off Heater turns on A thermostat is a device for regulating the temperature of a system so that the system's temperature is maintained near a desired setpoint temperature. AC turns off AC turns on
Time Lag • The term time lag effect refers to the delay between the time of an intervention or exposure onset, such as the date on which a person begins smoking cigarettes, and the subsequent development of a health outcome, such as the diagnosis of lung cancer.
Bibliography • ESS Guide Book • www.google.com • http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi • www.trafficforum.ethz.ch/budapest/ppt/SandersBudapest.ppt • http://searchfiletype.com/3-System-Feedback-loop-fs218915.html