Quantum Electron Configurations: An Interactive Guide
330 likes | 373 Vues
Dive into the world of quantum physics with this animation explaining electron configurations based on the principles of Schrödinger and Bohr. Explore orbitals, energy levels, and electron counts in different types of orbitals. Simplify complex electron configurations and understand the filling order. Discover the fascinating world of isoelectronic species and test your knowledge with the Ishihara Color Blindness Test.

Quantum Electron Configurations: An Interactive Guide
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Erwin Schrödinger 1887 - 1961
Werner Heisenberg 1901 – 1976
Bohr Theory The electron is a particle that must be in orbital in the atom. Quantum Theory The electron is like a cloud of negative energy or a wave. Orbitals are areas in 3D space where the electrons most probably are. The energy of the electron is in its vibrational modes- like notes on a guitar string. Photons are produced when high energy modes change to lower energy modes
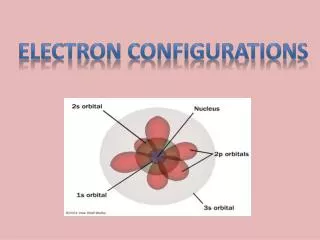
S orbitals Each orbital holds 2 electrons
P orbitals There are 3 suborbitals Each contains 2 electrons Total electrons = 6 Animation
D orbitals • There are 5 suborbitals • Each contains 2 electrons • Total electrons = 10
F orbitals There are 7 suborbitals Each contains 2 electrons Total electrons = 14
Quantum Periodic Table F 2p5 2s2 1s2 Count the electrons in each different orbital type until you get to Fluorine. Put in order of lowest to highest energy level.
1. F The Electron Configuration 1s22s22p5 Principle Quantum Number Number of Electrons in the Orbital Orbital Type- s, p, d, or f
Quantum Periodic Table 2p6 3p6 2s2 3s2 4s2 1s2 Ca
2. Ca 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 1s22s22p63s23p6 4s2 2 8 8 2 Simplify to a Bohr electron configuration
Quantum Periodic Table 2p6 3p6 3d9 2s2 3s2 4s2 1s2 Cu
3. Cu 1s22s22p63s23p63d94s2 Simplify to a Bohr electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p63d9 4s2 2 8 17 2
Quantum Periodic Table 2p6 3p6 3d10 4p6 2s2 3s2 4s2 1s2 Kr Count the electrons in each different orbital type until you get to Kr. Put in order of lowest to highest energy level.
4. Kr 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p6 Simplify to a Bohr electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 4s24p6 2 8 18 8
Quantum Periodic Table 2p6 3p6 3d10 4p6 4d4 2s2 3s2 4s2 5s2 1s2 Mo
4. Mo 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d45s2
Quantum Periodic Table 2p6 3p6 3d10 4p6 5p5 4d10 2s2 3s2 4s2 5s2 1s2 I
5. I 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p5 Simplify to a Bohr electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 4s24p64d10 5s25p5 2 8 18 18 7
Why does the 4s fill before the 3d? 5s 4p 3d 4s 3p 3s
Quantum Periodic Table 2p6 3p6 3d10 4p6 5p6 4d10 4s2 2s2 3s2 5s2 1s2 Ba2+
6. Ba2+ • 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p6 • Xe • 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p6 • I- • 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p6 • The above chemical species are isoelectronic- same • electron configuration
Ishihara Test for Colour Blindness – if you can read all of the numbers you have good colour vision Atomic Theory Song