MD5 Cracking
330 likes | 623 Vues
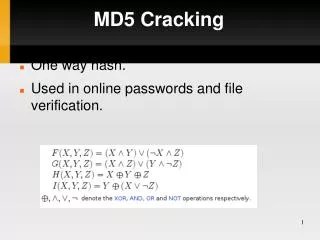
MD5 Cracking. One way hash. Used in online passwords and file verification. Lets destroy an MD5 hash. Lets use “steiner” Md5('steiner')= 7bfd4d773bec1249bb691bbad9d968a8 Input into rcrack. ./rcrack *.rt -h 7bfd4d773bec1249bb691bbad9d968a8 Wait. MD5 hashing. Tables vary greatly in size.

MD5 Cracking
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MD5 Cracking • One way hash. • Used in online passwords and file verification.
Lets destroy an MD5 hash • Lets use “steiner” • Md5('steiner')= • 7bfd4d773bec1249bb691bbad9d968a8 • Input into rcrack. • ./rcrack *.rt -h 7bfd4d773bec1249bb691bbad9d968a8 • Wait
MD5 hashing • Tables vary greatly in size. • Each added character add's exponential growth • md5_loweralpha-numeric_1-8 • 36.4 GB
General Wireless Vulnerabilities • Invasion and resource stealing • Traffic redirection • Denial of service • Rogue access points
Goals • Confidentiality • Prevent casual eavesdropping • Access control • Protect access to network infrastructure • Data integrity • Prevent tampering with transmitted messages
Logistics • A key is shared between the client and access point • Key length is 40 bits or 104 bits • Keys are static and whenever a key changes, all clients must update
WEP Implementation of RC4 • Checksum of the plain text is computed to provide data integrity • 24 bit Initialization vector (IV) is used to increase the size of the secret key • IV also makes it harder to crack by changing the key stream every time • IV is pre-pended to the cipher text, that way client can decrypt the message
WEP Authentication • Client sends message to access point (AP) requesting authentication • AP sends plain text stream to client • Client chooses IV and encrypts plain text stream • Client sends IV and cipher text to AP for verification
Database Attack • Some access points allow traffic to be encrypted or unencrypted • Hacker sends packets to the access point broadcast messages, AP responds with encrypted version • Hacker records key stream and puts it in database for later use • When client gets sent message with IV that is in the database, hacker XORs the two to get the plain text
Key Scheduling Attack • Some IVs are weak and through statistical analysis can reveal information about the key • Active attack involves de-authenticating client repeatedly until enough packets have been received to analyze • Utilizes the fact that several bytes of IP traffic can be easily predicted
Message Injection • Hacker can listen to authentication process and determine a key stream for a particular IV • Using this key stream, hacker can create packets and inject them into the network • WEP allows for IVs to be reused without triggering an alarm
Linux Security Distributions • Several live CDs are available that contain all tools necessary to hack WEP • Common applications include: • Aircrack Suite- wesside-ng- aireplay-ng- aircrack-ng • Airsnort • Kismet
Newer Security Protocols • Stop using WEP and use a newer protocol like WPA • Make you password harder to crack by using the maximum number of characters and using random ASCII characters ***(deprecated)***
Authentication • Evil Twin Attack • Hacker can force user off the AP, then use the same SSID to pose as the AP • How do you know who has control of an access point? • Enterprise systems can use a server to authenticate users
Other Suggestions • Wireless IDS • Can monitor network to prevent rogue access points • If attacker attempts to break into wireless LAN, the IDS can triangulate his location • Use end to end encryption • VPNs
Demo • Locate target • Do research • Get AP MAC and client MAC • Input into wesside-ng • If necessary, spoof a clients MAC
Lan Manager (LM) Hashes • Used by Microsoft • Windows passwords are stored using this algorithm • Only hashes 7 characters at a time. • Makes cracking considerably easier
Lets break my windows • Get Hash • Input into ophcrack • wait