Covalent and Metallic Bonds
150 likes | 320 Vues
Covalent and Metallic Bonds. How are these two items different?. Covalent bonds. Metallic bonds. Covalent Bonds. Most things are held together with covalent bonds. Characteristics. Usually low melting points Brittle in solid state. Ex: Oxygen low boiling point

Covalent and Metallic Bonds
E N D
Presentation Transcript
How are these two items different? Covalent bonds Metallic bonds
Covalent Bonds • Most things are held together with covalent bonds.
Characteristics • Usually low melting points • Brittle in solid state • Ex: Oxygen • low boiling point • Gas at room temperature. Ex: Wood: Brittle
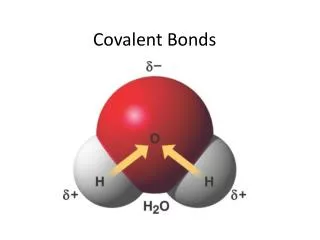
Covalent Bond • Atoms share one or more electrons • Nonmetals need energy to transfer electrons, so 2 nonmetals will not transfer electrons but share them to fill the valence shells.
Covalent Bonds and Molecules • Substances made form covalent bonds consist of individual particles called molecules. • A molecule consists of two or more atoms joined in a definite ratio. • Most molecules are composed two or more elements- like water.
Electron Dot • One way to represent atom and molecule bonding is with an electron-dot diagram • The diagram only shows the valence electrons of an atom. • Can help you predict how an atom may bond
Covalent Compounds and Molecules • An atom is to an element As A molecule is to a compound
Simplest Molecules • The simplest molecules contain 2 bonded atoms • Diatomic • The elements Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Fluorine, Oxygen, Iodine, Chlorine, and Bromine are always found as diatomic molecules:
More complex Molecules • Soap, plastic,& proteins are all complex molecules. Carbon is the base for a lot of these because it has a valence shell of 4.
Metallic Bonds • Metals can be shaped because of metallic bonds. • A metallic bond is formed by the attraction between positive charged metal ions and the electrons in the metal. • The positive ions form as the metals lose electrons.
Movement of Electrons throughout a Metal • Bonding in metals happens because the atoms are so close the outer energy shells overlap. This allows the valence electrons to “travel” throughout the metal
Properties of metals • Explain what each of the following are: • Conductivity • Ductility • Malleability • Why can metals be bent without breaking?