E E 2315
200 likes | 339 Vues
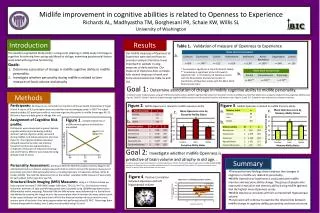
This lecture covers the fundamentals of mesh current analysis, a crucial technique in circuit theory. By focusing on mesh currents rather than branch currents, we simplify the circuit analysis process. The Mesh Current Method results in fewer equations and expresses all variables in terms of mesh currents, fully defining the circuit's behavior. Examples illustrate applying Kirchhoff's Voltage Law (KVL) across different meshes, using Ohm’s Law, and introducing forced meshes and supermesh techniques to tackle complex circuits efficiently.

E E 2315
E N D
Presentation Transcript
E E 2315 Lecture 05 -Mesh Current Analysis
Introduction to Mesh Current Method • More direct than branch equations • Fewer equations to solve • Express all variables in terms of mesh currents • Solution is set of mesh currents • Solution completely defines the circuit • Most Convenient Method to Model Magnetic Coupling (E E 2446 Topic)
Mesh Current Example 1 (1/2) KVL at Mesh 1: KVL at Mesh 2: Using Ohm’s Law:
Mesh Current Example 1 (2/2) Above linear equations can be solved for mesh currents I1 and I2.
Mesh Current Example 1a (1/2) KVL at Mesh 1: KVL at Mesh 2: Solve:
Mesh Current Example 2 (1/2) KVL @ Mesh 1: KVL @ Mesh 2: But:
Mesh Current Example 2 (2/2) Solve for I1 and I2:
Mesh Current Example 2a (1/2) KVL @ Mesh 1: KVL @ Mesh 2: But:
Mesh Current Example 2a (2/2) Solve for I1 and I2:
Forced Mesh (1/2) • No KVL equation possible for mesh 2 • But I2 is known: I2 = Is
Forced Mesh (2/2) KVL for mesh 1: Substitute and Solve:
Forced Mesh Example 3a KVL for mesh 1: Substitute and Solve:
Supermesh Example (1/5) • No KVL possible for meshes 1 or 2 • Use Supermesh (dotted loop) for KVL
Supermesh Example (2/5) Supermesh KVL: Mesh 3 KVL:
Supermesh Example (3/5) Also: Subst for I2:
Supermesh Example (4/5) And: Rearranging the equations: