Respiration
170 likes | 327 Vues
Respiration. - an introduction for GCSE. by S J Freedman Merchant Taylors’ School, Crosby. What is respiration ?. Breathing ? NO ! Sweating ? NO !. What is respiration ?. oxidising food releasing energy ...similar to burning. The main points.

Respiration
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Respiration - an introduction for GCSE by S J Freedman Merchant Taylors’ School, Crosby
What is respiration ? • Breathing ? • NO ! • Sweating ? • NO !
What is respiration ? • oxidising food • releasing energy • ...similar to burning
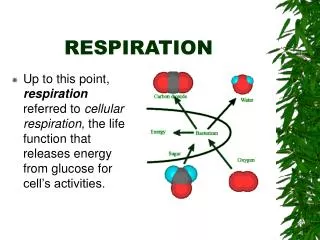
The main points • Food (usually glucose, a sugar) “burns” using oxygen • releasing useful energy • producing carbon dioxide and water as waste products
In other words... GLUCOSE oxygen ENERGY carbon dioxide & water Click to continue
Is that all there is to it ? you should be so lucky...
GLUCOSE energy PYRUVIC ACID oxygen ENERGY carbon dioxide & water There are two main stages... ANAEROBIC AEROBIC Click to continue
But... Pyruvic acid is VERY poisonous !
GLUCOSE ANAEROBIC energy oxygen ENERGY AEROBIC carbon dioxide & water So it has to be destroyed! PYRUVIC ACID
energy So it has to be destroyed! GLUCOSE ANAEROBIC And so, of course, it can’t be oxidised to release all that lovely energy!
That depends what sort of organism you are What happens to it ? Plant Animal Microbe Click on the picture to find out or here to move on
Animals (in their muscles) make LACTIC ACID
Ouch! The lactic acid is a pain! It’s what makes muscles hurt when they’ve been used a lot - so much, in fact, that they can’t get oxygen fast enough and have to respire… ANAEROBICALLY
Plants and microbes make CARBON DIOXIDE and ETHANOL
CO 2 Yeast • Yeast is a FUNGUS. • It respires anaerobically • to make carbon dioxide. • and ETHANOL
Some useful links • Introduction • Aerobic respiration • Anaerobic respiration • Fermentation – anaerobic respiration in microbes. Return to start Finish