Science Starter!
90 likes | 264 Vues
This guide explores the analysis of an object's motion through data interpretation from position vs. time graphs. It covers motion phases including stops, constant forward velocity, and constant backward velocity. Key calculations include determining the object's total distance traveled (50 m), displacement from 0 to 30 s (10 m), and average speed and velocity across the graph segments. The importance of understanding slopes, average speed, and acceleration in motion analysis is emphasized. Ensure comprehension of key concepts such as positive and negative slopes for directionality in motion.

Science Starter!
E N D
Presentation Transcript
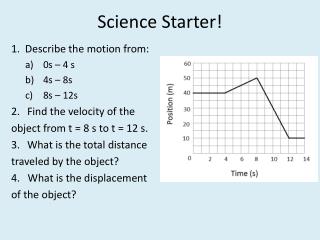
Science Starter! 1. Describe the motion from: • 0s – 4 s • 4s – 8s • 8s – 12s • Find the velocity of the object from t = 8 s to t = 12 s. • What is the total distance traveled by the object? 4. What is the displacement of the object?
1. a) 0s – 4 s STOPPED b) 4s – 8s Constant Velocity (FORWARD) c) 8s – 12s Constant Velocity (BACKWARD) 2. Find slope: (10 – 50) m = - 10 m/s (12-8) s 3. 50 m 4. - 30 m
Analyzing “x vs. t” graphs 1. What is the total distance traveled by the object from t= 0s to t = 30 s? 30 m 0 m TOTAL = 50 m 20 m 2. What is the displacement of the object from t= 0s to t = 30 s? t = 0s: object is at 0 m t = 30s: object is at 10 m Δ x = x – xo Δ x = 10 – 0 = + 10 m
Average Speed On the graph shown, determine the average speed from t = 0s to t = 30s.
Average Velocity On the graph shown, determine the average speed from t = 0s to t = 30s.
Average Velocity (Slope Method) On the graph shown, determine the average velocity from t = 0s to t = 30s. Draw a line connecting the two points. 2. Find the slope of this line: (10 – 0) m = + 0.33 m/s (30 – 0) s
Describe the motion depicted in this particle model. • Create a data chart and graph the motion shown.
Acceleration Rate at which the velocity of an object changes. Vector Symbol: “a” Unit: m/s2
Key Ideas to Remember On a “Position vs. Time” graph: ∙ Linear Line: Constant Velocity - Positive Slope: Moving in (+) Direction (forward) - Negative Slope: Moving in (-) Direction (backward) - Zero Slope: Not Moving (stopped) * Speed: Distance / Time *Velocity: Displacement / Time - Average Velocity: Slope between any two points - Must include either (+) or (-) ∙ Curved Line: Acceleration