Interoperability and Supply Chain
260 likes | 391 Vues
This work explores how service integration and information interoperability can revolutionize the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) supply chain. It addresses significant issues such as fragmented communications, lack of information sharing, and inefficient workflows. By proposing a scalable mega-service model, the research aims to enhance decision-making, reduce costs, and improve efficiency during the virtual design and construction process. Key areas of focus include existing problems, a structured approach to service integration, and potential funding sources to support these initiatives.

Interoperability and Supply Chain
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Interoperability and Supply Chain Kincho H. Law, Gio Wiederhold, Charles Han, Jack Cheng
The big idea Service Integration and Information Interoperability, which can be leveraged to - establish a scalable mega-service for AEC virtual supply chain - facilitate the virtual design and construction process - enhance workflow efficiency, decision-making and cost saving.
Overview • Motivating Engineering/Business Problem • Point of Departure • Research Methods • Service Integration • Information Interoperability • Relationship to CIFE Goals • External Involvement • Research Schedule, Milestone and Risks • Potential Funding Sources
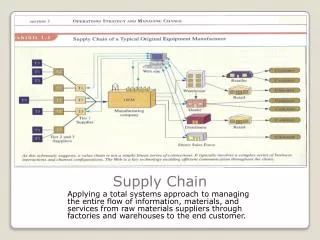
Owner Architect/ Design Consultants General Contractor Subcontractors Suppliers Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Motivating Engineering/Business Problem Current AEC Supply Chain Courtesy: Hans Bjornsson
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Observations of Current AEC Supply Chain • Fragmented AEC supply chain • Lack of information sharing • Scattered information sources • Various software and hardware platforms • Different goals and objectives of project participants
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Consequences and Drawbacks • Increased lead-time • Decreased corporation and system accountability and transparency • Excess Ordering (Bullwhip Effect) • Reduced customer service level Can it be improved? Service Integration & Information Interoperability
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Point of Departure (1/3) SCM Tools Not Designed for AEC Industry Examples of Supply Chain Management (SCM) applications: • IBM • SeeCommerce • FreeMarkets • Oracle • SAP • Ariba • Manugistics • I2 • Visual SourceSafe • ComponentSoftware RCS • SoftBench CM • Forte Code Management • Remedy Change Management Manufacturing Industry(large trading partners,stable supply chains) AEC Industry(scattered relatively small partners,project-based temporary supply chains)
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Point of Departure (2/3)Interoperability Besides Product Description STEP Application Protocols Part 201 Explicit Drafting Part 202 Associative Drafting Part 203 Configuration Controlled Design Part 204 Mechanical Design Using Boundary Representation Part 205 Mechanical Design Using Surface Representation Part 206 Mechanical Design Using Wireframe Representation Part 207 Sheet Metal Dies and Blocks Part 208 Life Cycle Product Change Process Part 209 Design Through Analysis of Composite and Metallic Structure Part 210 Electronic Printed Circuit Assembly, Design and Manufacturing Part 211 Electronics Test Diagnostics and Remanufacture Part 212 Electrotechnical Plants Part 213 Numerical Control Process Plans for Machined Parts Part 214 Core Data for Automotive Mechanical Design Processes Part 215 Ship Arrangement Part 216 Ship Molded Forms Part 217 Ship Piping Part 218 Ship Structures Part 219 Dimensional Inspection Process Planning for CMMs Data Exchange Standards (e.g. STEP, IFC) for Product Description Do Exist How about Data Definition for Cost Estimation, Project Mgt, Supply Chain, Product Lifecycle Mgt (PLM)?
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Point of Departure (3/3)Languages Not Engineering-Oriented Examples of Services Description Languages: • SWSF (Semantic Web Services Framework): {language, ontology} • FLOWS (First-order Logic Ontology for Web Services) • ROWS (Rules Ontology for Web Services) • WSDL (Web Services Description Language) • BPEL4WS (Business Process Execution Language for Web Services) • UDDI (Universal Description, Discovery and Integration) • OWL-S (OWL ontology for web services) • PSL (process specification language) • WSML (Web Services Modeling Ontology) (WSML – OWL, WSML) • BPSS (ebXML’s Business Process Specification Schema) • WSFL (Web Services Flow Language) • Wf-XML, XPDL, XLANG Business Oriented Not designed to support AEC applications(from Design, Engineering, Constructionto Operational Activities)
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Research Methods • Two basic work packages: • Service Integration Framework Distributed engineering and web services Composition / specification language • Information Interoperability Knowledge-Driven Approach for Information Analysis Semantic similarities and differences
<?xml version="1.0"?> <WeatherReport> <weather date="2003-9-23"> <location> <zipcode value="33410" /> </location> <conditions value=" Isolated thunderstorms early, mainly cloudy overnight with a few showers" /> <temperature> <templow c="23.3" f="74.0" /> <temphigh c="32.2" f="90.0" /> </temperature> …… </weather> …… Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Example 1: Integrating Online Weather Service to Engineering Simulation Microsoft Excel Autodesk ADT
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Rescheduling and Re-simulating of Project Original Schedule in Primavera P3 Updated Schedule in Primavera P3 Updated Backlog Chart Simulated using Vite and Displayed in Excel Original Backlog Chart Simulated using Vite and Displayed in Excel
Deployed Suppliers Web Services Web Service Gateway Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Example 2: Integrating Online Catalog with CAD and Inventory Management Web Services ROQs Order & Invoice Architectural Design Inventory Management Automated Procurement Further Simulation
Autodesk’s i-drop : web page modified HTML file enabled object XML package file Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Interoperability with Online Resources
Deployed Suppliers Web Services Web Service Gateway Inventory Mgt & Cost Estimation Procurement Availability Checking & Decision-making Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Inventory Management and Procurement Automated Workflow/ Supply Chain
Service 1 Service 3 Service 1 Service 3 Mega- Service Service 4 Service 2 Service 4 Service 2 Service 5 Service 5 Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Integration of Engineering and Web Services Benefits of mega-service: • Increased functionality of simulation system • Modularity in system development • Scalability in complex supply chain Software Framework includes: • Mechanisms integrating distributed services • Languages specifying process scenario
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Knowledge-Driven Approach for Information Analysis Domains of Information Interoperability: • Engineering, Manufacturing, Business, … Ontologies– Terminological basis for information exchange meaningful information exchange and sharing Heterogeneous Representation of Ontologies: • Term Difference (Elevator vs. Lift) • View/Contextual Difference (Transportation vs. Equipment) • Schema Difference (BPEL vs. PSL vs. WSML vs. etc.) • Version Difference (IfcWorkTask – IFC 2.0 vs. IfcTask – IFC 2x) Building a single, unifying model of concepts and definitions will never be practical[Source: Steve Ray (Division Chief, NIST Manufacturing Systems Integration Division) ]
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Mediation for Information Articulation • Mediation semantic differences of formats • Metadata are defined and extracted Terms useful for linking rules Result contains shared terms Mediation Source Domain 2: Owned and maintained by Organization B Source Domain 1: Owned and maintained by Organization A
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Schema Mapping Schema (1) Integrated Schema (Metadata) Schema (2) ONLY: Keyword / Term Matching
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Advanced Text and Data Mining Techniques (Content Analysis) Relatedness Analysis Discover Related Concepts among Heterogeneous Ontologies for Interoperability? Regulation 1 Regulation 2
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Relationship to CIFE Goals • Engineering Modeling Methods: • Modeling of product, process and organization data for information exchange and sharing • Analysis Methods: • Establishment of mega-service framework to enhance scheduling, resources allocation, cost estimation and procurement efficiency • Incorporation of online information into engineering simulation • Business Metrics: • Support for information flow and global supply chain • Strategic Management: • Integration of distributed information and services for decision-making • Economic Impact Analysis: • Efficient interoperability leading to reduced inventory, improved customer service and increased corporation transparency and accountability
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals External Involvement • Potential Interest from industry organizations and government agencies (e.g. ECPIP – Engineering and Construction Project Information Platform) • Identified Collaborations: • Prof. Arto Kiviniemi (VTT Technical Research Center of Finland) • Prof. Hans Bjornsson (Chalmers, Sweden) • Dr. Kent Reed (NIST, IAI’s ifc & CIS/2 Interoperability project) • Dr. Mark Palmer (NIST, FIATECH’s AEX Interoperability project) • Dr. Ram Sriram (NIST Manufacturing Systems Integration Division)
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Research Tasks, Schedule and Milestone
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Risks • Establishment of a comprehensive information system infrastructure is a task beyond a 1- or 2-year seed research proposal • Pilot project can lead to fundamental understanding • Wrapping existing software applications into autonomous services and integrating the tools can be challenging Collaborations with other researchers and their organizations
Plan, Risk, Funding Motivating Problem Point of Departure Service Integration Interoperability CIFE Goals Potential Funding Sources • Government funding opportunities: National Science Foundation, NIST, others • NIST (as well as FIATECH): • “Information interoperability and supply chain management” Upcoming key initiative • Significant funding and supports has been proposed • Collaborated with and received funding from NIST in the past Potential funding support is anticipated
THE END Questions and Answers