Genotypic and Phenotypic Ratios
160 likes | 450 Vues
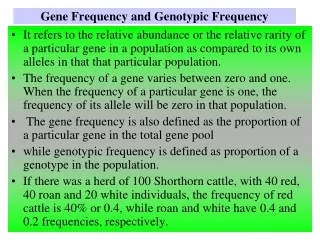
Genotypic and Phenotypic Ratios. Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment. Genotypic and Phenotypic Ratios. What were the genotype and phenotype ratios of crossing a homozygous dominant green pea pod colour with a homozygous recessive yellow pea pod colour?. Cross GG x gg ?

Genotypic and Phenotypic Ratios
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Genotypic and Phenotypic Ratios Law of Segregation and the Law of Independent Assortment
Genotypic and Phenotypic Ratios • What were the genotype and phenotype ratios of crossing a homozygous dominant green pea pod colour with a homozygous recessive yellow pea pod colour? • Cross GG x gg? • The F1 genotype ratio for the offspring is 0 GG: 4Gg : 0 gg • The F1 phenotype ratio is 4 green: 0 yellow
Genotypic and Phenotypic Ratios Vocabulary: G = dominant allele is green g = recessive allele is yellow GG = homozygous dominant genotype gg = homozygous recessive genotype Now what happens when the heterozygous F1 generation is crossed with itself?
Genotypic and Phenotypic Ratios Cross F1 x F1 • The genotypic ratio is 1GG : 2Gg : 1gg • The phenotypic ratio is 3 green : 1 yellow
Mendelian Laws • Law of Segregation • States that inherited traits are determined by pairs of genes and that each of the genes separates into separate gametes • Law of Independent Assortment • States that inheritance of one trait does not effect the inheritance of alleles for another trait
Dihybrid crosses • Dihybrid crosses are made when phenotypes and genotypes with 2 independent alleles are analyzed. • Process is similar to monohybrid crosses. • The Punnett square now has 16 boxes to represent the 16 possible genotypes in the offspring
Steps for solving dihybrid cross problems • Step 1: Figure out the genotypes of the parents. • Step 2: Figure out what kinds of gametes the parents can produce. • Step 3: Set up a Punnett Square for your cross. One set of gametes go across the top and the other, down the column. • Step 4: Fill in the offspring inside the table. • Step 5: Figure out the genotypic ratios for your predicted offspring. • Step 5: Figure out the phenotypic ratios for your predicted offspring.
Example 1 • Free earlobes are controlled by the dominant allele E and attached earlobes are controlled by the recessive allele, e. • A widow’s peak is controlled by the dominant allele H, while a straight hair line is determined by the recessive allele h. • What would be the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring of a free earlobed, widow’s peak male and a free earlobed, widow’s peak female ?
Step 1: Figuring out the genotypes • What would be the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring of a heterozygous free earlobed, widow’s peak male and a heterozygous free earlobed, widow’s peak female ? • Genotypes: • Male – EeHh • Female – EeHh
Step 2: Figuring out the Gametes • Need to use the FOIL rule Genotype: EeHh Possible gametes: EH, Eh, eH, eh
Step 3-4: Do Punnett’s Square P1 P2 EH Eh eH eh EH Eh eH eh
Step 5: Figuring out the Genotypic ratios Genotypic ratios • EEHH 1:16 • EEHh 2:16 • EeHH 2:16 • EeHh 4:16 • Eehh 2:16 • eeHH 1:16 • eeHh 2:16 • eehh 1:16 • EEhh 1:16
Step 6: Figuring out the Phenotypic ratios Red= free earlobes, widow’s peak,9/16 Black=free earlobes, straight hair line 3/16 Brown= attached earlobes, widow’s peak 3/16 Blue= attached earlobes, straight hair line 1/16 Note that there is a 9:3:3:1 phenotypic ratio. 9/16 showing both dominant traits 3/16 & 3/16 showing one of the recessive traits 1/16 showing both recessive traits.