Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
260 likes | 408 Vues
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis. DNA Structure. Chromosomes. Chromosomes are thread-like structures found in the nucleus of the cell. They contain DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). A molecule of DNA consists of two strands made up of repeating units called NUCLEOTIDES. A DNA Nucleotide. base.

Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis DNA Structure
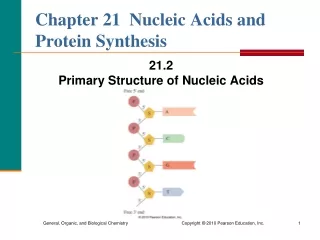
Chromosomes • Chromosomes are thread-like structures found in the nucleus of the cell. • They contain DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). • A molecule of DNA consists of two strands made up of repeating units called NUCLEOTIDES.
A DNA Nucleotide base phosphate deoxyribose sugar
Bases • There are 4 different bases therefore 4 different nucleotides • ADENINE (A) • GUANINE (G) • THYMINE (T) • CYTOSINE (C)
Base Pairs • To form a double strand the bases pair up. • Adenine always pairs with Thymine • Cytosine always pairs with Guanine
Bonds • Hydrogen bonds form between bases. • Strong chemical bonds form between the phosphate group of one molecule and the deoxyribose sugar of another.
Replication Requirements • DNA TEMPLATE • 4 TYPES OF NUCLEOTIDES • ENZYMES (DNA polymerase) • ATP for energy
DNA Replication DNA unwinds DNA unzips and H bonds break Free nucleotides find complementary partner, H bonds form Strong chemical bonds form and DNA winds back up
Semi-Conservative Replication Original strand New strand
Coding • Bases code for amino acids. • Amino acids code for proteins • The sequence of bases that are unique to the organism.
An RNA Nucleotide base phosphate ribose sugar
DNA Double Strand Thymine base pairs with adenine Deoxyribose Sugar RNA Single Strand Uracil base pairs with adenine Ribose Sugar DNA and RNA Differences
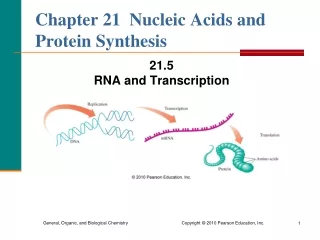
Types of RNA • Messenger RNA (mRNA) – carries the genetic information from the nucleus to the cytoplasm for protein synthesis. (codon) • Transfer RNA (tRNA) – Carries amino acids on the anti-codon to the appropriate codon to form a polypeptide.
DNA – mRNA – tRNA - Protein Complete the sequences of mRNA and tRNA then using Torrance pg 344 find out the names of the amino acids. DNA - TTACGGCAATGCGGTACCGTTGGGGGCAG mRNA - Codons (set of 3 bases) tRNA - Anti-codons (set of 3 matching bases) Protein -
DNA – mRNA – tRNA - Protein DNA - TTACGGCAATGCGGTACCGTTGGGGGCAG mRNA - AAUGCCGUUACGCCAUGGCAACCCCCGUC Codons (set of 3 bases) tRNA - UUACGGCAAUGCGGUACCGUUGGGGGCAG Anti-codons (set of 3 matching bases) Protein - aspn– ala – val – thr – pro – try – glu – pro - pro
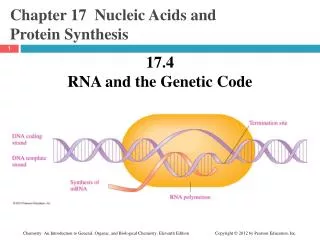
Stages in Transcriptionsheets pg 20 • DNA helix unwinds • DNA molecule unzips – weak H bonds break • mRNA nucleotides pair up with complementary base on DNA molecule • mRNA nucleotides loosely held in place by H bonds to DNA molecule • Enzyme forms bond between sugar and phosphate on mRNA nucleotides • mRNA bases become detached from DNA molecule • mRNA molecule leaves nucleus through pore in nuclear membrane • H bonds between DNA bases reform. DNA coils back up into double helix
Fate of Protein • The protein is carried in a vesicle from the RER to the Golgi where it is processed and packaged into a vesicle which fuses with the cell membrane.