Branches
120 likes | 356 Vues
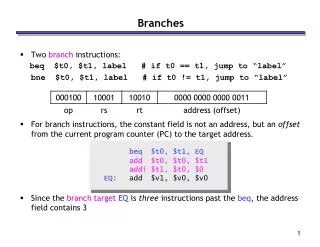
Branches. if statements in C if ( condition ) clause if ( condition ) clause1 else clause2 Rearrange 2nd if into the following: if ( condition ) branch to L1; clause2; branch to L2; L1: clause1; … L2:. Suffix. Description. Flags tested. EQ. Equal. Z=1.

Branches
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Branches • if statements in C • if (condition) clause • if (condition) clause1 else clause2 • Rearrange 2nd if into the following: if (condition) branch to L1; clause2; branch to L2; L1: clause1; … L2:
Suffix Description Flags tested EQ Equal Z=1 NE Not equal Z=0 CS/HS Unsigned higher or same C=1 CC/LO Unsigned lower C=0 MI Minus N=1 PL Positive or Zero N=0 VS Overflow V=1 VC No overflow V=0 HI Unsigned higher C=1 & Z=0 LS Unsigned lower or same C=0 or Z=1 GE Greater or equal N=V LT Less than N!=V GT Greater than Z=0 & N=V LE Less than or equal Z=1 or N=!V AL Always Condition Codes • The possible condition codes are listed below • Note AL is the default and does not need to be specified
ARM Branch Instructions Unconditional branch B (or BAL) branch always testing individual condition codes: bmi – branch on negative (N==1) bpl – branch on positive or zero (N==0) bvs– branch on overflow set (V==1) bvc – branch on overflow clear (V==0) bcs – branch on carry set (C==1) bcc – branch on carry clear (C==0)
ARM Branch Instructions testing result of compare or other operation (signed arithmetic): be –branch on equal (Z==1) bne–branch on not equal (Z==0) bls–branch on less than ((N xor V)==1) ble–branch on less than or equal ((Z or (N xor V))==1) bge–branch on greater than or equal ((N xor V)==0) bgt–branch on greater than ((Z or (N xor V))==0)
Comparison Instructions • CMP – Compare: subtracts a register or an immediate value from a register value and updates condition codes • Examples: • CMP r3, #0 ; set Z flag if r3 == 0 • CMP r3, r4 ; set Z flag if r3 == r4 All flags are set as a result of this operation, not just Z.
(true) (a+b)>c a+b > c? (false) a += b Exit C if statement in ARM if((a+b)>c) a+=b; • Use this mapping: a: r0, b: r1, c: r2, sum:r3 • ARM code: add r3,r0,r1 cmp r3, r2 blefalse @ branch to false when((a+b)>c) is false add r0, r0, r1 @ a = a+bfalse:
(false) i != j (true) i == j i == j? f=g+h f=g-h Exit C if statement in ARM if(i == j) f=g+h; else f=g-h; • Use this mapping: f: r0, g: r1, h: r2, i: r3, j: r4
(false) i != j (true) i == j i == j? f=g+h f=g-h Exit C if-else in ARM • if (i == j) • f=g+h; else • f=g-h; • ARM code: cmp r3, r4 @ Z = 1 if i==j beq true @ branch to true when i==j sub r0,r1,r2 @ f = g-h (false) b done @ branch to done true: add r0,r1,r2 @ f = g+h (true) done:
Conditional execution in ARM An unusual ARM feature is that all instructions may be conditional: CMP r0, #5 @ if (r0 != 5) { ADDNE r1, r1, r0 @ r1 := r1 + r0 - r2 SUBNE r1, r1, r2 } • this removes the need for some short branches, improving performance and code density
Loops in C/Assembly while loop assume this mapping: @ a: r0, b: r1 while ( a <= 17 ) test: { cmp r0, #17 a = a + b; bgtdone } add r0, r0, r1 b test done:
Loops in C/Assembly for loop @ a: r0, b: r1, c: r2 for ( a = 1; a <= b; a++ ) mov r0, #1 { test: c *= a; cmp r0, r1 } bgt done mul r2, r2, r0 rewritten as while loop add r0, r0, #1 a = 1; b test while ( a <= b ) done: { c *= a; a++; }
Loops in C/Assembly Three ways to do a counted loop: for loop, counted up from 0 to n-1 @ i: r0, n: r1 for ( i = 0; i < n; i++ ) { clr r0 <body> test: } cmp r0, r1 bge done rewritten as while loop <body> i = 0; add r0, r0, #1 while ( i < n ) b test { done: <body> i++; } for loop, counted up from 1 to n for ( i = 1; i <= n; i++ ) { mov 1, %i_r <body> test: } cmp %i_r, n bg done nop rewritten as while loop <body> i = 1; while ( i <= n ) { inc %i_r <body> ba test i++; nop } done: for loop, counted down from to n to 1 for ( i = n; i > 0; i-- ) { mov n, %i_r <body> test: } cmp %i_r, 0 ble done nop rewritten as while loop <body> i = n; while ( i > 0 ) { dec %i_r <body> ba test i--; nop } done: