Tissues
291 likes | 659 Vues
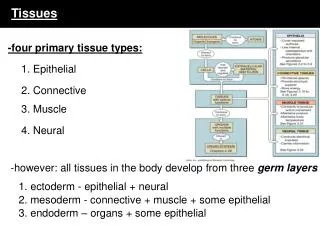
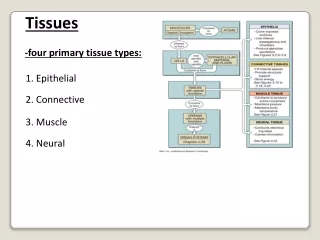
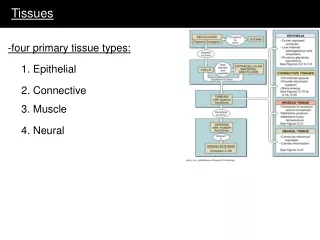
Tissues. Cells specialize – heart, liver, skeletal muscle, stomach, etc. If loss of indispensible cells, deadly Tissue – groups of cells similar in structure and function Epithelium - covering Connective - support Nervous - control Muscle - movement. Lining, covering, and glandular tissue

Tissues
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Cells specialize – heart, liver, skeletal muscle, stomach, etc. If loss of indispensible cells, deadly • Tissue – groups of cells similar in structure and function • Epithelium - covering • Connective - support • Nervous - control • Muscle - movement
Lining, covering, and glandular tissue • Glands in body • Covers all free body surfaces • Skin, lines cavities • Separates us from outside • All substance make and absorb pass through • Functions • Protection - skin • Absorption – small intestine • Filtration - kidneys • Secretion - glands
Fit closely together • Desmosomes • Tight Junctions • Basement membrane • Structureless, secreted by both epithelial cells and connective tissue • Apical surface – all have one free edge • Some smooth, some microvilli, cilia • Avascular – rely on capillaries in connective tissue for food and oxygen • Regenerate easily Figure 3.17
Figure 3.17a • Two classifications • # of layers • Shape of cells • Simple Epithelia most common with absorption, secretion, filtration • Very thin – not protective • Stratified Epithelia • Named for apical surface • Primarily protective
Figure 3.18a • Single layer, close together • Membranes where filtration or exchange of substances by rapid diffusion occurs • WHERE? • Serous membranes • Slick membranes that line ventral cavity and cover organs
Cubed shape, single layer, basement membrane Common in glands and ducts – salivary glands and pancreas, kidney tubules, and ovaries Figure 3.18b
Tall cells, single layer, basement membrane Line digestive tract from stomach to anus Mucous membranes – membranes that line cavities open to exterior Figure 3.18c
Some cell shorter than other, nuclei at different heights All cells on basement membrane Absorption and secretion Ciliated version lines respiratory tract – propels mucus Figure 3.18d
Figure 3.18e • Most common stratified epithelia • Close to surface cells are squamous, near basement membrane cuboidal or columnar • Sites of abuse or friction • Esophagus, mouth, outer layer of skin
Stratified Cuboidal • Typically 2 layers with surface layer being cuboidal • Stratified Columnar • Surface cells columnar • Basal cells vary • Both rare in body, found in ducts of large glands
Figure 3.18f Modified stratified squamous Lines urinary bladder, ureters, and part of urethra Cells slide past each other allows stretching as urine enters.
Gland consists of one or more type of cell that secretes a product • Exocrine Gland – Ducts, secrete products through ducts to epithelia, external and internal – sweat glands, pancreas • Endocrine Gland - Ductless glands, secrete product into blood for transport Figure 3.18f
Protecting, supporting and binding together • Characteristics • Extracellular Matrix – nonliving, outside cell • Most well vascularized • Exceptions – tendons and ligaments poor blood supply, cartilages are avascular – heal slowly
# of cells in relation to matrix varies • Extracellular Matrix – water reservoir for body • Nonliving substance outside the cell • Produced by Conn. Tissue cells and secreted • Ground substance – water, adhesion proteins – attach to fibers, charged polysaccharides – trap water as intertwine. • Fibers – various types • Collagen – white fibers, high tensile strength • Elastic – yellow fibers, stretch and recoil • Reticular – fine collagen fibers, form internal “skeleton” of soft organs
Osseous tissue • Bone cells surrounded by hard matrix • Matrix made of • Calcium salts and large amounts of collagen fibers Figure 3.19a
Figure 3.19b More flexible than bone Most abundant Collagen fibers hidden by glassy matrix Supporting structure like larynx, attaches ribs to bone, and covers heads of bone at joints Skeleton of fetus
Figure 3.19c Forms cushion like discs that separate vertebrae of spinal column.
Structure where elasticity is needed Examples?
Figure 3.19d • Collagen fibers as main matrix element • Fibroblasts – fiber forming cells • Lower layers of dermis • Form rope-like structure • Tendons – muscle to bone • Ligaments – bone to bone at joints
Softer, more cells, less fibers Cobwebby tissue, cushions and protects organs Holds internal organs together and in place Body part inflamed, this tissue soaks up fluid and swells. What is this called? Figure 3.19e
Fat • Oil droplet fill most of cell, compresses nucleus • Protects some organs – kidneys and eyes • Storages – breasts and hips for fuel • Subcutaneous tissue beneath skin • Insulates and protects from bumps and heat changes Figure 3.19f
Reticular fibers and cells • Forms stroma which can support free blood cells • Lymphocytes in lymphoid organs like spleen, lymph nodes, and bone marrow Figure 3.19g
Figure 3.19h Blood cells surrounded by fluid non-living matrix (plasma) Fibers are soluble, only visible during clotting event Unique connective tissue
Attach to bone Voluntary Striated Multinucleate Long cylindrical Often called muscle fibers Figure 3.20a
Figure 3.20b Found only in heart Pumps and propels blood Involuntary Striated Uninucleate Branched cells that fit together at intercalated discs
No striations Uninucleate Spindle shaped Found in walls of hollow organs – stomach, intestines Contracts more slowly that others, Peristalsis Figure 3.20c
Figure 3.21 Irritability and conductivity major function Neurons – Cytoplasm stretched out as much as 3 feet, conduct signals over long distance Supporting cells – insulate, support and protect neurons