9.5 Hyperbolas
170 likes | 531 Vues
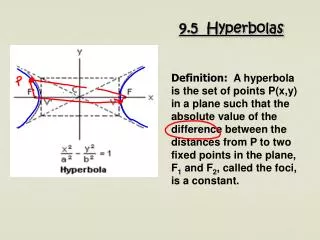
9.5 Hyperbolas. Definition: A hyperbola is the set of points P(x,y) in a plane such that the absolute value of the difference between the distances from P to two fixed points in the plane, F 1 and F 2 , called the foci, is a constant. 9.5 Hyperbolas. Transverse axis Conjugate Axis

9.5 Hyperbolas
E N D
Presentation Transcript
9.5 Hyperbolas Definition: A hyperbola is the set of points P(x,y) in a plane such that the absolute value of the difference between the distances from P to two fixed points in the plane, F1 and F2, called the foci, is a constant.
9.5 Hyperbolas Transverse axis Conjugate Axis Vertices Co-vertices Center Foci Asymptotes (2a) length ofVto V (2b) length of CV to CV Endpoints of TA Endpoints of CA Intersection of the 2 axes Lie on inside of hyperbola Horizontal Vertical (When centered at the origin)
9.5 Hyperbolas • Notes: • a2 is always the denominator of the ________ term when the equation is written in standard form. • _________ axis can be longer or ____________ • The length of the transverse axis is _________ • The length of the conjugate axis is _________ • a2 + b2 = c2 1st Either shorter 2a 2b
Example 1: Write the standard equation of the hyperbola with vertices (-4,0) and (4,0) and co-vertices (0, -3) and (0, 3). Sketch the graph.
Example 2: Write the standard equation of the hyperbola with V(-7, 0) (7, 0) and CV (0,-4) (0, 4).
Example 3: Write the standard equation of the hyperbola with F (-1, 1) (5, 1) and V (0, 1) (4, 1).
Don’t forget! x and h are BFFs! So are y and k! Don’t split them up! Example 4: Write the standard equation of the hyperbola with F (3, -3) (3, 7) and V (3, -1) (3, 5).
Example 5: Find the equation of the asymptotes and the coordinates of the vertices for the graph of Then graph the hyperbola.
Example 6: The equation x2 – y2 –6x –10y –20 = 0 represents a hyperbola. Write the standard equation of the hyperbola. Give the coordinates of the center, vertices, co-vertices, and foci. Then graph the hyperbola.
Example 7: The equation –2x2 + y2 + 4x + 6y + 3 = 0represents a hyperbola. Write the standard equation of the hyperbola. Give the coordinates of the center, vertices, co-vertices, and foci. Then graph the hyperbola.
Example 8: The equation 4x2 – 25y2 – 8x + 100y – 196 = 0represents a hyperbola. Write the standard equation of the hyperbola. Give the coordinates of the center, vertices, co-vertices, and foci. Then graph the hyperbola.