Human Skeleton
220 likes | 746 Vues
Human Skeleton. Skeleton?. The skeleton is a supportive framework that maintains the shape of humans and protects our internal organs. It also plays a vital role in our ability to move around. Endoskeleton.

Human Skeleton
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Skeleton? • The skeleton is a supportive framework that maintains the shape of humans and protects our internal organs. • It also plays a vital role in our ability to move around.
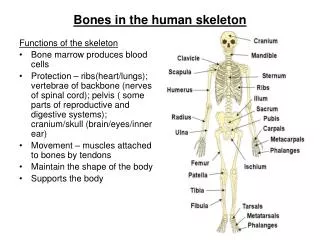
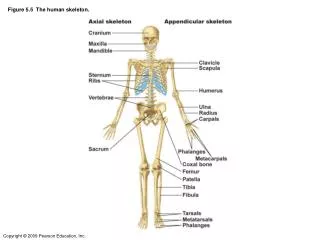
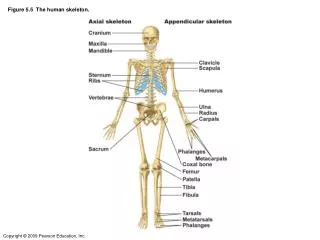
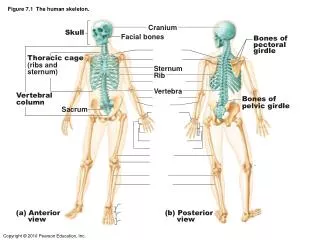
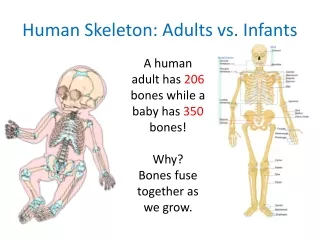
Endoskeleton • Humans have a bony endoskeleton made up of 206 bones, although we are born with more than 300. • The skeleton is divided into two parts: axial and appendicular skeleton.
Axial Skeleton • Consists of the skull, backbone, and the ribcage. • Forms the upright axis of the body. • Protects the brain, spinal cord, and the organs in the chest.
Axial Skeleton The axial skeleton makes up 80 of your 206 bones and can be broken down into three areas: the skull (cranium), the backbone (spine), and the bony thorax (ribcage).
The skull provides the framework for most of your sensory organs and is considered as the most important structure in your skeleton. The bony thorax is basically your chest, made up of your ribs and sternum. You have twelve ribs that help protect your lungs and heart. The backbone is actually a flexible structure made up of 26 bones. It is approximately 28 inches long and separated into 5 regions.
Appendicular Skeleton • Consist of the upper and lower limbs, and the pectoral (shoulder) and pelvic (hip) girdles. • Pelvis is adapted for an upright stance. • Lower limbs support the upper body and enable walking. • Upper limbs are used for manipulation.
Three types of bone • Periosteum: A glistening double layered tissue that covers the hard bone. • Compact bone: Seems very hard to the naked eye, but is very hollow. • Spongy bone: Houses the red bone marrow and the yellow bone marrow
What is the difference between red and yellow bone marrow? • Red bone marrow is what makes red blood cells. The majority of the red bone marrow for an adult is located in the head of the femur and the humerus. • Yellow bone marrow is stored fat. This marrow can sometimes turn into red bone marrow when a person is very anemic.
What are the five main functions of bones? Protection Support Blood cell formation Movement Storage
How many bones are in the human skull? • 10? • 15? • 20? • What is your guess???? There are 22 bones in the human skull, not including the three in the inner ear
What is the purpose of so many bones? • Cranial bones surround and protect the brain. • Facial bones provide attachment points for facial muscles, openings for eating and breathing, cavities for the sensory organs, and anchorage for the teeth.
Names of all the bones • Frontal bone • Nasal bone • Lacrimal bone (2) • Ethmoid bone (2) • Nasal spine • Supraorbital ridge • Glabella • Parietal bone (2) • Mandible • Maxilla • Vomer • Mastoid process • Zygomatic bone • Occipital bone • Temporal bone (2) • Sphenoid bone (2) • External auditory meatus
Directionality Anterior view Lateral View Inferior view Interior view