Understanding the Endocrine System: Hormones and Major Organs
190 likes | 287 Vues
Explore the functions, major organs, and disorders of the endocrine system, including pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, adrenals, pancreas, and gonads. Learn about hyperfunction and hypofunction cases of various glands.

Understanding the Endocrine System: Hormones and Major Organs
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Endocrine System By: CarlyCrute 5-13-11 3rdperiod
Function of the Endocrine sytem • Secrete horemones which coordinates and directs the activities of target cells and target organs.
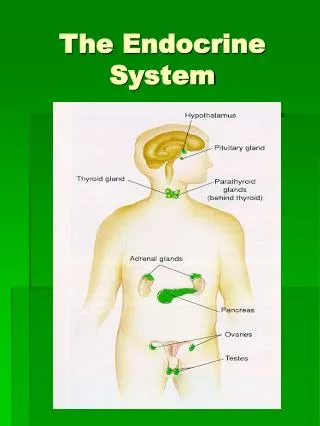
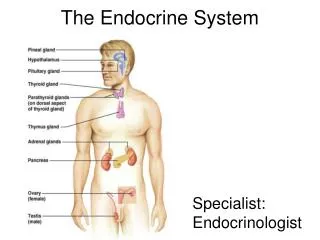
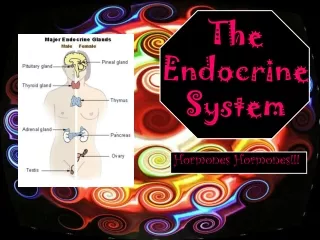
Major Organs • The major organs are the pituitary, pineal, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, adrenals, pancreas, and the gonads.
Pituitary gland (Master Gland) • 10 mm of weight and the size of a grape. • Located at the base of the brain. • Hormones it secretes are GH, TSH, ACTH, MSH, FSH, LH, ICSH, Oxytocin, and ADH
Pineal Gland • Base of the brain. • Pinecone shaped. • Secretes the hormone Melatonin.
Thyroid Gland • Lower portion of anterior neck. • Secretes T4, T3, and Thyrocalcitonin. • Butterfly shaped.
Parathyroid Gland • Posterior surface of thyroid gland. • Secretes Parathormone. • Size of a grain of rice.
Thymus Gland • Under the Sternum. • Secretes Thymosin. • Fairly large at childhood then begins to disappear at puberty.
Adrenal Gland • Superior surface of each kidney. • Secretes Adrenaline, Glucocorticoid, Aldosterone, and sex hormones.
Pancreas • Behind the stomach. • Secrets Insulin and Glucagon.
Gonads • Ovaries: Located in the female pelvis. • Secretes Estrogen and progesterone. • Testes: Located in the male scrotum. • Secretes Testosterone.
Hyperfunction of the Pituitary Gland • Gigantism: Overgrowth of long bones excessive tallness. • Acromegaly: Adult hood. Overdevelopment of bones of the face hands and feet. Chin protrudes and lips, nose, and extremities enlarge.
Hypofunction of the Pituitary Gland • Dwarfism: Growth of long bones are decreased. Sexually immature and physique remains juvenile. • Diabetes Insipidus: Excessive thirst. Drop in the amount of ADH.
hyperthyroidism • Exophtalmos: Bulging pupils.
hypothyroidism • Myxedema: Face is swollen weight increases and memory failed. • Cretinism: Lack of physical and mental growth.
Parathyroid • Tetany: Twitchings, spasms.
Hyperfunction of the Adrenal Gland • Cushings syndrome: Tumor or prolonged use of Prednisone. High blood pressure, muscular weakness, obesity, poor helaing of skin lesions, bruise easily, excessive hair growth, menstrual disorders, hyperglycemia.
Hypofunction of the Adrenal Gland • Addisons disease: Excessive pigmentation of the skin, decreased levels of blood glucose, hypoglycemia, low blood pressure, muscle weakness, fatigue, weight loss, diarrhea, vomiting. • Diabetes Mellitus: Polyuria, polydypsia, polyphagia, weight loss, blurrevission, and possible diabetic coma.