Hormones and Homeostasis
501 likes | 1.56k Vues
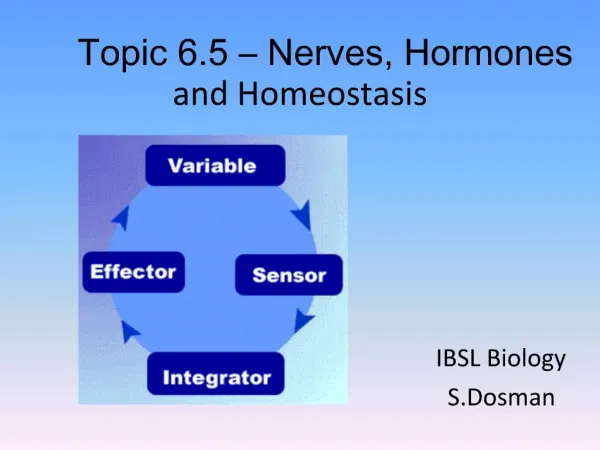
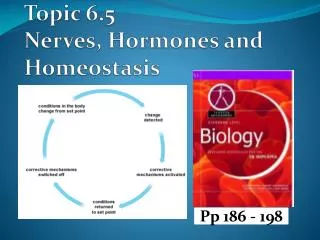
Hormones and Homeostasis. IB Biology Topic 6. Group Activity. Which group can come up with the biggest list of hormones you have already come across in biology? You have 2 min!. Negative Feedback control. Involuntary responses. Mechanisms of temperature regulation are involuntary

Hormones and Homeostasis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Hormones and Homeostasis IB Biology Topic 6
Group Activity • Which group can come up with the biggest list of hormones you have already come across in biology? • You have 2 min!
Involuntary responses • Mechanisms of temperature regulation are involuntary • Controlled at a subconscious level by the hypothalamus
Vasodilation • Skin becomes dilated • Large volume of blood flows through capillaries near skin surface • Blood able to lose heat by radiation
Increase in rate of sweating • Heat energy from body • Convert sweat into water vapour • Lowers body temperature
Vasoconstriction • Arterioles leading to skin become constricted • Small volume of blood flow to surface capillaries • Little heat lost by radiation
This means less heat is lost from the surface of the skin If the temperature falls, the blood vessel constricts (gets shut off).
Decreased rate of sweating • Sweating reduced to a minimum • Heat conserved
Contraction of erector muscles • Wide layer of air trapped between body and external environment • Air poor conductor of heat • Layer of insulation reduces heat loss
Voluntary responses • Body temperature drops below normal • Nerve impulses transmit this information to cerebrum • Person ‘feels cold’ • Takes appropriate action to correct problem -puts on a jacket -has a cup of tea etc.
EVERYONE (except Alonso!) • Write down as a group EVERYTHING you know or heard about diabetes under these three headings • The science of the disease • The lifestyle change for the individual • The cure/medication Then Alonso or I will check it! Not This Cure!!
Control of blood sugar level • Living cells need a continuous supply of energy • Most of this energy released by oxidation of glucose • Cells using up glucose present in bloodstream (blood sugar)
Homeostatic Mechanism • Body only obtains supplies of glucose when food is eaten • Need to guarantee regular supply of glucose regardless of how often food is consumed • Body employs a homeostatic mechanism
The Liver • 100g of glucose stored as glycogen in the liver • Glucose can be added or removed from this reservoir of stored carbohydrate
Rise in blood sugar level • Detected by βcells in regions of pancreas called Islets of Langerhans • Receptor cells produce insulin • Hormone transported in bloodstream to the liver • Insulin activates an enzyme which catalyses glucose glycogen • Blood sugar concentration brought down to normal
Drop in blood sugar level • Detected in α cells by Islets of Langerhans • Release the hormone glucagon • Glucagon transported to the liver and activates a different enzyme which catalyses the reaction • glycogen glucose
Diabetes mellitus • 2 types of diabetes • Type I diabetes • Type II diabetes
Type I diabetes • Insufficient insulin produced Causes body produces antibodies against insulin and/or βcells in Islets of Langerhans Treatment Inject insulin (why can´t you just take a tablet?) Transplant pancreas or βcells
Type II diabetes • Insufficient insulin produced • Body cells become less sensitive to insulin Causes Obesity, age, familiyhistory Treatment Eatlesscarbs Exercise and lose weight Medication (lowerbloodglucose and increaseinsulinproduction)
Absence of insulin • Cells unable to use glucose efficiently • Fat stores become depleted • Weight loss • Tissue wastage