Atomic Orbitals
80 likes | 270 Vues
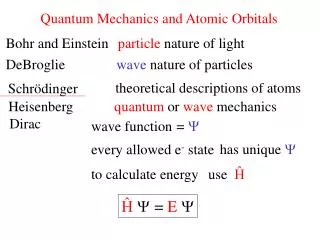
Atomic Orbitals. Schrodinger’s Quantum Mechanics Model. Orbitals – areas within atoms where there is a high probability of finding electrons. Principal Energy Levels - A region around the nucleus of an atom where the electron is likely to be moving . ( n = 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , etc .)

Atomic Orbitals
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Atomic Orbitals Schrodinger’s Quantum Mechanics Model
Orbitals – areas within atoms where there is a high probability of finding electrons • Principal Energy Levels - A region around the nucleus of an atom where the electron is likely to be moving. (n = 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , etc.) • Number 1-7 on periodic table down side.
Energy sublevels • Energy sublevels can be thought of as a section of seats in a theater. The rows that are higher up and farther from the stage contain more seats, just as energy levels that are farther from the nucleus contain more sublevels. • Sublevels are labeled s, p, d, and f according to the shapes of the atom’s orbitals.
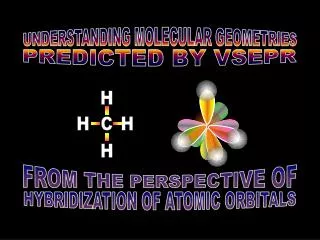
Atomic Orbitals • Each orbital may contain at most 2 electrons. • Each energy level may contain at most 1 s orbital, 3 p orbitals, 5 d orbitals, and 7 f orbitals. (all odd numbers).
Label and outline the s, p, d, and f blocks on the PT as shown below (any 4 colors)
Practice: read like a book • Hydrogen (1 electron) : 1s1 • Helium(2 electrons): 1s2 • Lithium(3 electrons): 1s2, 2s1 • Beryllium(4 electrons): 1s2. 2s2 • Carbon(6 electrons): 1s2, 2s2, 2p2 • Iron(26 electrons): 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6, 4s2, 3d6 • You try: Sulfur ( ___ electrons): _____________________ • Bromine (___ electrons): _______________________
More practice • Do page 9 that you got yesterday. “Practice #1 – electron configuration”