Understanding Spin and Helicity in Quantum States with Electromagnetic Interactions
100 likes | 266 Vues
This text explores the concept of spin for particles at rest and not at rest, emphasizing the two-fold degeneracy that implies the existence of a commuting operator with eigenvalues that label the states. The discussion extends to helicity eigenvalues and the effects of boosting on spin in arbitrary frames. Additional focus is on zero mass fermions, specifically neutrinos, highlighting their behavior under parity and the implications for positive and negative helicity states in the Weyl basis. The inclusion of electromagnetic interactions and the non-relativistic limit are also considered.

Understanding Spin and Helicity in Quantum States with Electromagnetic Interactions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
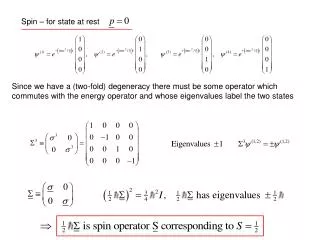
Spin – for state at rest Since we have a (two-fold) degeneracy there must be some operator which commutes with the energy operator and whose eigenvalues label the two states
Spin – for state NOT at rest Helicity Eigenvalues (More generally, in arbitrary frame, spin given by boosting result at rest -
Nonrelativistic limit Dominant time dependence large component small component
Spin – for state at rest Since we have a (two-fold) degeneracy there must be some operator which commutes with the energy operator and whose eigenvalues label the two states
Spin – for state NOT at rest Helicity Eigenvalues (More generally, in arbitrary frame, spin given by boosting result at rest -
Zero mass fermions – the two component neutrino Weyl basis For m=0 …no mixing Both have +ve and –ve energy solution Negative helicity neutrino - LH Positive helicity antineutrino - RH Projects LH neutrino
Parity Parity invariant (neutrinos violate parity)