802.11b Modulation Scheme
120 likes | 950 Vues
802.11b Modulation Scheme. Presented By: Nishant Divecha. Evolution of the 802.11b. Major Problems at the Physical Layer caused by nature of the chosen media that had to be addressed in 802.11b Bandwidth allocation; External interference; Reflection. .

802.11b Modulation Scheme
E N D
Presentation Transcript
802.11b Modulation Scheme Presented By: Nishant Divecha
Evolution of the 802.11b Major Problems at the Physical Layer caused by nature of the chosen media that had to be addressed in 802.11b • Bandwidth allocation; • External interference; • Reflection.
The physical layer of the original 802.11 standardized three wireless data exchange techniques: • Infrared (IR); • Frequency hopping spread spectrum (FHSS); • Direct sequence spread spectrum (DSSS).
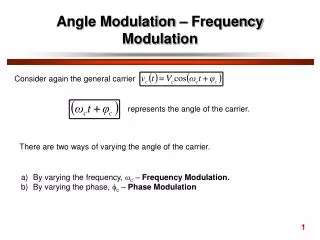
802.11 DSSS Radio Interface • 1 Mbps 1 Msymbol/s BPSK spread by 11 chip Barker code, (-4 dB Bandwidth = 11 MHz, main lobe = 22 MHz), IEEE 802.11 • 2 Mbps 1 Msymbol/s QPSK spread by 11 chip Barker code (-4 dB Bandwidth = 11 MHz, main lobe = 22 MHz), IEEE 802.11 • 5.5 Mbps 2 Msymbol/s QPSK like symbols spread by 8 chip Complementary Code Keying (CCK). IEEE 802.11b • 11 Mbps 4 Msymbol/s QPSK like symbols spread by 8 chip Complementary Code Keying (CCK). IEEE 802.11b • 54 Mbps OFDM with max. 52 sub-carriers, IEEE 802.11a / IEEE 802.11g
1 Mbps (802.11), 1 bit/symbol ; 2 symbol valuesDBPSK, 11 analog chips 2 Mbps (802.11), 2 bit/symbol 4 symbol values DQPSK ; 11 analog chips
5.5 Mbps (802.11b) 4 bit/symbol ; 16 symbol values DQPSK ; 8 analog chips 11 Mbps (802.11b) 8 bit/symbol ; 256 symbol values DQPSK ; 8 analog chips