SET TOP BOX
170 likes | 507 Vues
SET TOP BOX. What is set-top box ? An interactive device which integrates the video and audio decoding capabilities of television with a multimedia application execution environment. It provides a user friendly interface offering personalized multimedia services and regular cable TV service.

SET TOP BOX
E N D
Presentation Transcript
SET TOP BOX What is set-top box ? An interactive device which integrates the video and audio decoding capabilities of television with a multimedia application execution environment. It provides a user friendly interface offering personalized multimedia services and regular cable TV service.
Digital video networks(DVN) • Digital television advantage. • Digital video delivery requirements • High bandwidth. • Fibre cable, satellite, broadcast and computer networks can be used. • Traditional cable networks analogue systems and their drawbacks. • Satellite and terrestrial networks. • Internet suitability for interactive network and drawback.
DVN need to deliver a high bandwidth stream into consumer homes and a low bandwidth communication layer for interaction between the STB user and the service provider. • Cable operators approach for DVN. • Need to extend unidirectional coaxial networking with a communication path from subscriber home to cable service gateways that can control the content being sent to subscriber. • Advantage of video compression technology. • Constraints with cable networks.
Telephone companies approach. • Advantage with telephone companies. • Already have set up for P2P and technology for control and service gateways to manage wide area switched star networks. • Drawback. • Low bandwidth between head end equipment and consumer’s home.
Video dial tone network. • Designed with fibre optic backbone with coaxial cable or fibre optic cable to the home. • Figure. • Has two types of networks • Unidirectional broadband network to distribute video and audio as MPEG-2 transport packets over ATM. • Bidirectional TCP/IP low speed signalling network.
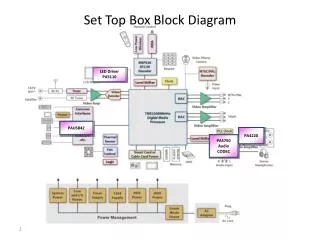
Set Top Box Hardware Architecture. • Requirements based on functionality. • Should have MPEG-2 sub-system to decode MPEG-2 video and audio. • Should enable user to download custom applications and execute them on the STB which requires a general purpose microprocessor in the STB with an architecture that supports control of the different devices. • Various hardware components. • Figure.
STB software architecture For personalized interactive services, a set top box should be addressable in the video dial-tone network, thus providing P2P communication between a video and information provider and a user. It should also have the ability to download client applications and execute them locally. The control software on the set top box ties together all the hardware components into a functioning unit.
STB software has two parts. • System software which provides the DAVID application programming interface. • Application software that provides cable TV functionality or some other personalized multimedia service. • DAVID system software includes. • Operating system(os-9) kernel. • Device drivers. • File manager. • Operating system(os-9) kernel is responsible for the following: • Scheduling different tasks for the microprocessor. • Managing inter-process communication between different tasks and processes in the STB. • Memory management for the multi-tasking operating system. • Maintaining the real time clock for the system.
Device drivers The various hardware components of STB have programmable registers that can be used to control the behaviour of the components. Each one of these devices has a device driver task associated with it that allows the main microprocessor to manage the device. The device drivers also perform interrupt servicing for the components and hide the details about device addresses and actual register values. • File manager • File manager available for each device driver and provides a ‘file like’ interface for the device. • ‘file like’ interface provides a uniform layer of abstraction and is generic to all the capabilities of STB. • RTNFM, SPF, MPFM, AUXMAN.
Application Software. • interoperability of softwares. • Navigator. • Downloaded applications. • Operating system upgrade. • Other resident applications: config, display
Conclusion For the hardware there will be strong trend towards very flexible decoders in the form of signal processors and fast CPU’s possibly even combined with even combined in one large digital processing CPU. The arrangements for sending information from terminal(STB) into the network can be improved both in latency and in throughput. The graphic subsystem is likely to grow towards 3D applications. STB software hides the machine and network specific features of a set top box under a layer of abstraction and provides a user friendly interface to access cable television and video information services. The software components are likely to increase with more integration and more programmable components. This will increase the flexibility of STB.