Understanding Acids and Bases: Properties, Examples, and Uses
70 likes | 211 Vues
Acids and bases are fundamental chemical substances with distinctive properties. Acids, characterized by a sour taste, react with metals and carbonates, and turn blue litmus paper red, often containing H+ ions. Common examples include hydrochloric acid and citric acid. In contrast, bases have a bitter taste, feel slippery, and turn red litmus paper blue, typically containing OH- ions. Accessibly utilized in daily life, acids are found in fruits, while bases are crucial in cleaning products and baking. Understanding their roles aids in their applications across industries.

Understanding Acids and Bases: Properties, Examples, and Uses
E N D
Presentation Transcript
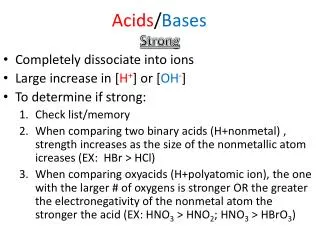
Acids • Is a substance that tastes sour, reacts with metals and carbonates, and turns blue litmus paper red. • Usually with H+ ions • Examples: orange, apple, fruit juice. • Examples: • hydrochloric acid (HCl) • nitric Acid (HNO3) • sulfuric acid (H2SO4) • carbonic acid (H2CO3) • acetic acid (C2H4O2).
Acid Traits • Taste sour (lemon juice) • Reacts with metals • This is the reason behind corrosion, acids eat away metals • Reacts with carbonates (CO32-) • Turns blue litmus paper red (an indicator of color change).
Bases • A substance that taste bitter, feels slippery, and turns red litmus paper blue. • Opposite of acids • Typically has OH- ions. • Examples: • Sodium hydroxide • Calcium hydroxide • ammonia
Bases Traits • Taste bitter • Examples: • Soap • Shampoo • Detergents • Slippery Feel • Ex: Soap • Reaction with Indicator • Red litmus turns blue • Other reactions • Don’t react with carbonates
Uses of Acids • Found in many fruits • Lactic acid, produced by muscles, causes soreness • Nitric acid and phosphoric acid found in fertilizers • Acid to clean bricks • Sulfuric acid in batteries
Uses of Bases • Calcium oxide and calcium hydroxide help make cement and mortar • Calcium oxide is used by gardeners to make the soil less acidic • Ammonia is used to as a cleaner • Baking soda used for cooking to fluff up breads and cakes.