SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY IN Rana pipiens
230 likes | 614 Vues
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY IN Rana pipiens. BIOL 305L. Midterm Exam: Friday, March 15 th during lab lecture No calculators Format: multiple choice, short ans, essay, fill in blank, T/F No labs that week! NO MAKEUP EXAM UNLESS UNIVERSITY APPROVED EMERGENCY

SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY IN Rana pipiens
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Midterm Exam: Friday, March 15th during lab lecture No calculators Format: multiple choice, short ans, essay, fill in blank, T/F No labs that week! NO MAKEUP EXAM UNLESS UNIVERSITY APPROVED EMERGENCY Old midterm will be posted online next week. Use it to TEST what you know. Do NOT memorize answers!! ANNOUNCEMENTS
ANNOUNCEMENTS • Study for Midterm: • Background concepts/theory • Experimental results (expected) • Flow of information/experimental set up (be able to draw) • Names & function of all instruments • Anatomy (name of muscles, organs, nerves and organisms) • Lab exercises (handouts), especially the introduction • Observations in lab • Traces produced using LabScribe (be able to draw) • Any/all graphs made (i.e. Excel graphs) • Notes from lab lead off lecture
REVIEW: THE SCIATIC NERVE Main Points: • Mixed Nerve • Stimulus Artifact • Threshold • Compound Action Potential • Recruitment • Maximum Recruitment • Conduction Velocity • Bidirectionality • Effect of temperature
THIS WEEK: SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY The Dissection: • Isolation of frog: Instrumentation & Equipment:
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY • The Stimulus: • iWorx Unit • Stimulating • Electrode
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY The Response: • Relative force of muscle contraction measured by deflection of force transducer blade
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY Motor Unit: • Unit of contraction in intact organisms • Composed of:
slice from spinal chord motor neuron axons in a nerve leading from spinal chord muscle neuromuscular junction
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY “Us” versus Them: • Vertebrate Skeletal Muscle: • A motor neuron innervates a muscle fiber • A muscle fiber is innervated by • AP in motor neuron is
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY “Us” Versus Them: • Invertebrates (Arthropods): • A motor neuron can innervate a muscle fiber • Multiple motor neurons may innervate • motor neurons exist
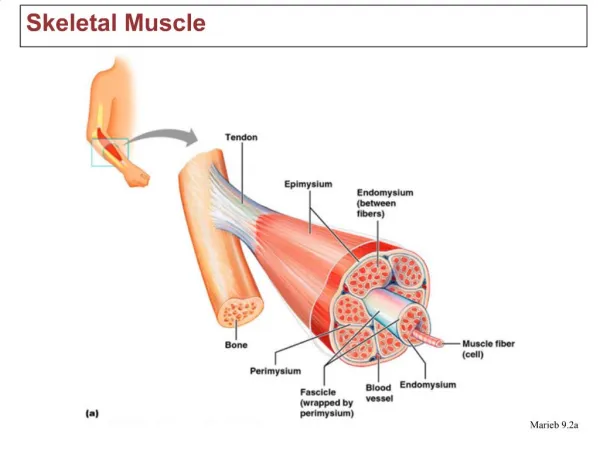
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY Gastrocnemius Muscle: • In intact organisms, innervated by • Sciatic nerve will be removed in lab • You will stimulate muscle DIRECTLY • Contractile force measured with
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY Two Methods to Increase Contractile Force: • Increase Stimulus : • Illustrates • Increase Stimulus : • Illustrates
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY Recruitment: • As stimulus intensity increases, more muscle fibers reach threshold and contract • The greater number of muscle fibers recruited, the greater
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY Recruitment: • A muscle reaches MAXIMUM RECRUITMENT when
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY Temporal Summation: • In lab, we’ll also observe the relationship between stimulus frequency and force of contraction
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY Single twitch Single Twitch • Single contraction • If multiple twitches occur
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY Summation: • Sustained contraction due to • Muscle only • Results in
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY Tetanus: • State of • Muscle does • Results in contraction of
SKELETAL MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY Fatigue: • Some types of muscle fibers
MUSCLE FIBER TYPES • Different Muscle Cell Types Differ in Susceptibility to Fatigue (as well as threshold, contractile strength, etc..) • Slow versus Fast Twitch Muscle Fibers
MUSCLE FIBER TYPES Slow twitch (oxidative; aerobic)
MUSCLE FIBER TYPES Fast twitch (glycolytic; anaerobic)