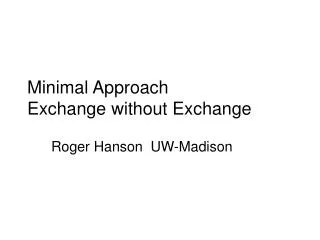The ABIM Practice Improvement Module (PIM) for Residency Programs
200 likes | 318 Vues
The ABIM Practice Improvement Module (PIM) empowers residency programs to enhance clinical skills through systematic patient care analysis. It emphasizes functional anatomy in medical practice while focusing on asthma, diabetes, preventive cardiology, and more. The PIM involves a structured learning cycle where residents audit charts, gather patient survey data, and reflect on feedback to create actionable improvement plans. This comprehensive approach helps identify care gaps, fosters a systems-based practice, and cultivates valuable management skills essential for contemporary healthcare settings.

The ABIM Practice Improvement Module (PIM) for Residency Programs
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The ABIM Practice Improvement Module (PIM) for Residency Programs
Functional Anatomy of a PIM Survey Patients Review Charts Analyze Practice Collect Data Data Synthesized and Returned Develop Improvement Plan Develop Practice Improvement Plan P A Impact D Implement and Test Change S
ABIM PIM Topics • Asthma • Diabetes • Preventive Cardiology • Clinical Preventive Services • Hypertension • Care of the Vulnerable Elderly • Hospital Care (JCAHO measures) • Subspecialty PIMs (2006) • May be especially good for fellows
Learning (Improvement) Cycle Deliver Care Measure Care Make a Change Reflect on Feedback
Practice Improvement Module – Step 1 Deliver Care Chart Audit Patient Survey Practice Survey Measure Care Make a Change Reflect on Feedback
Practice Improvement Module – Step 2 Deliver Care Chart Audit Patient Survey Practice Survey Measure Care Make a Change Performance Report Guided Reflection Reflect on Feedback
Practice Improvement Module – Step 3 Deliver Care Chart Audit Patient Survey Practice Survey Ideas to Change System Measure Care Make a Change Performance Report Guided Reflection Reflect on Feedback
Practice Improvement Module – Step 4 New Process to Deliver Care Deliver Care Chart Audit Patient Survey Practice Survey Ideas to Change System Measure Care Make a Change Performance Report Guided Reflection Reflect on Feedback
Purpose of PIM Chart Audit • Physician self assessment • Competence in practice-based learning and improvement • Systematic analysis of care processes under physician’s control • Experience with data collection and management for population-based medicine
DEC 2002 230 105 43 98
Patient Survey • Invite patients to complete a questionnaire • Automated telephone or web • Confidential and anonymous • Provides valuable and specific information about specific aspects of care • Logistically most difficult in residency clinic setting
Examine Practice Systems • Builds awareness of systems-based practice • Residents often unaware of what “systems” exist in clinic • Identifies level of health information technology • Identifies practice staff organization and teamwork • Stimulates ideas for improvement
Review Report and Develop a Plan • Download practice performance analysis compared to guidelines • Select opportunities for improvement • Develop a plan for improvement • Report the impact of the test through re-measurement
50 60 80 80
Availability • PIMs available now • Web-based • $100 registration plus $25 dollars per resident • 5 medical record audits/resident with a minimum of 25 • 5 patient surveys/resident • Will score at 25 regardless of total number of residents • One practice assessment