Prime Factorization
330 likes | 776 Vues
Prime Factorization. 2-2. http://www.brainpop.com/math/numbersandoperations/factoring/. Brainpop - Factoring video .. Answer the questions. http://www.brainpop.com/math/numbersandoperations/factoring/ quiz/. Answers : C D B A A D C B C A. Factor.

Prime Factorization
E N D
Presentation Transcript
http://www.brainpop.com/math/numbersandoperations/factoring/ Brainpop - Factoring video .. Answer the questions
http://www.brainpop.com/math/numbersandoperations/factoring/quiz/http://www.brainpop.com/math/numbersandoperations/factoring/quiz/ Answers: C D B A A D C B C A
Factor The numbers that are multiplied to get a product • 15 = 3 x 5 • 3 and 5 are factors of 15 2 x 9 = 18 2 & 9 are factors of 18 3 x 2 =6 3 & 2 are factors of 6
Prime Number is a counting number that only has two factors, itself and one. • One is not a prime 7 is a prime 5 is a prime
Composite Number Counting numbers which have more than two factors (such as six, whose factors are 1, 2, 3 and 6) • One is not a composite 8 is a composite 55 is a composite
A Rhyme to Help Us Remember Prime number Prime number What do you see? I see no other factors Except for one and me. Composite number Composite number What do you see? I see at least three factors Including one and me.
All of the orange numbers on this chart are prime. Write them down. Refer to them so you don’t waste time trying to factor them.
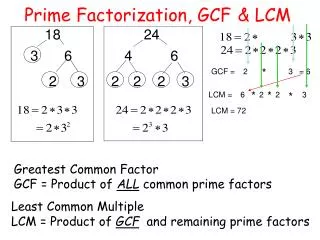
Prime Factorization When a composite number is written as a product of all of its prime factors Using the Factor Tree 78 / \ / \ 2 x 39 / / \ / / \ 2 x 3 x 13
Let’s Try a Factor Tree! 84 / \ 2 x 42 / / \ 2 x 2 x 21 / / / \ 2 x 2 3 x 7
72 / \ 8 x 9 / \ / \ 2 x 4 x 3 x 3 / \ 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 72 / \ 2 x 36 / / \ 2 x 2 x 18 / / / \ 2 x 2 x 2 x 9 / / / / \ 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 Factor Trees do not look the same for the same number, but the final answer is the same.
Greatest Common Factor The largest common factor of 2 or more numbers GCF of 24 and 36 Is 12 Use prime factorization or ladder to find GCF GCF of 72 and 84 Is 12
72 / \ 8 x 9 / \ / \ 2 x 4 x 3 x 3 / \ 2 x 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 Take the common prime factors of each number and multiply to find the greatest common factor. 84 / \ 2 x 42 / / \ 2 x 2 x 21 / / / \ 2 x 2 3 x 7 2 x 2 x 3 = 12 Prime Factorization is helpful for finding greatest common factors.
Least Common Multiple The smallest product that both numbers have in common LCM of 5 & 7 Is 35 LCM of 4 & 10 is 20 LCM of 12 & 15 Is 60
72 6 = 84 7 Use the Ladder for LCM, GCF and Simplifying Fractions 2 72 84 WRITEthe two numbers on one line. 2 36 42 DRAW THE L SHAPE 3 18 21 DIVIDEout common prime numbers starting with the smallest 6 7 LCM = 2 2 3 6 7 = 504 LCMmakes an L: GCF = 2 2 3 = 12 GCFis down the left side: Simplified fraction is on the bottom
24 2 = 36 3 Use the Ladder for LCM, GCF and Simplifying Fractions WRITEthe two numbers on one line. 2 24 36 2 12 18 DRAW THE L SHAPE DIVIDEout common prime numbers starting with the smallest 3 6 9 2 3 LCM = 2 2 3 2 3 = 72 LCMmakes an L: GCF = 2 2 3 = 12 GCFis down the left side: Simplified fraction is on the bottom
6 2 = 9 3 Use the Ladder for LCM, GCF and Simplifying Fractions WRITEthe two numbers on one line. 3 6 9 2 3 DRAW THE L SHAPE DIVIDEout common prime numbers starting with the smallest LCM = 3 2 3 = 18 LCMmakes an L: GCF = 3 GCFis down the left side: Simplified fraction is on the bottom
5 5 = 7 7 Use the Ladder for LCM, GCF and Simplifying Fractions WRITEthe two numbers on one line. 5 7 5 7 DRAW THE L SHAPE DIVIDEout common prime numbers starting with the smallest LCM = 5 x 7 = 35 LCMmakes an L: GCF = 1 GCFis down the left side: Simplified fraction is on the bottom
HOMEWORK • PG 77 4 – 40 evens only 8-16 use ladder 26-32 use factor trees 34-40 use ladder method
Resources • Brain Pop – Prime Factors • Brain Pop - Prime Numbers • Brain Pop - Exponents
Interactive Practice for Factor Trees Virtual Manipulatives Interactive Practice 1 Interactive Practice from MathPlayground.com
The Birthday Cake Methoda.k.a. The Box Method An alternative to factor trees A video from YouTube
Challenge Problem • Use what you know about multiplying whole numbers by variables and exponents to make a factor tree for the following monomial 45x3 x3 45 9 5 x x x 3 3
A Random Thought about Prime Numbers Brought to you from YouTube.com
24 2 = 36 3 Use the Ladder for LCM, GCF and Simplifying Fractions WRITE the two numbers on one line. 2 24 36 2 12 18 DRAW THE L SHAPE DIVIDE out common prime numbers starting with the smallest 3 6 9 2 3 LCM = 2 2 3 2 3 = 72 LCM makes an L: GCF = 2 2 3 = 12 GCF is down the left side: Simplified fraction is on the bottom
Ch Test this ThursdayBig Rocks Quiz tomorrow – Decimal rules #1Four Sight paperHomework Practice sheet 2-1 evens only