Exploring Flower Structure and Plant Growth: Dicot vs. Monocot Differences
160 likes | 297 Vues
In this lesson, we dive into the intricate structure of flowers and the growth patterns of plants, focusing on dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants. Students will learn to draw and label diagrams showing tissue distribution in the stem and leaf of dicots, differentiate between dicots and monocots, and explore the roles of apical and lateral meristems in growth. Additionally, we will discuss the influence of auxin in phototropism and engage in group discussions to enhance understanding. A virtual experiment will also help visualize these concepts.

Exploring Flower Structure and Plant Growth: Dicot vs. Monocot Differences
E N D
Presentation Transcript
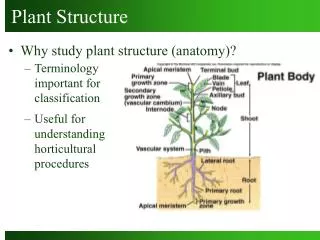
PlantStructure and Growth Topic 9 AHL IB BIOLOGY
LearningObjectives • Draw and labelplan diagrams to show the distribution of tissues in the stem and leaf of a dicotyledonous plant. • Outlinethree differences between the structures of dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants. • Comparegrowth due to apical and lateral meristems in dicotyledonous plants. • Explainthe role of auxin in phototropism as an example of the control of plant growth.
GROUP THOUGHT: Can youlist 3 differencesbetweenmonocots and dicots?
GROUP THOUGHT: Whydoesmowingthelawnnotkillthegrass? BONUS: Spot thegrammarmistake!
Watchthis virtual experiment What do youseehappenning? Why do youthinkthisishappenning?
PastPaperQuestion (a) apical and lateral (b) 2 max StructureMonocotyledonousDicotyledonus leaf parallel veins branched (net of) veins; seed one cotyledon two cotyledons; flower floral parts in multiple of 3 floral parts in multiple of 4 or 5; stem scattered vascular bundles ring of vascular bundles around central pith; root adventitious roots branched tap roots; Award [1] for each correct line (c)auxinproduced at apical meristem / tip; transported to growing area / zone of cell growth; lateral transport to cells on shade side; results in cellexpansion; shoot “grows” towards light source; experimental detail; 3 max