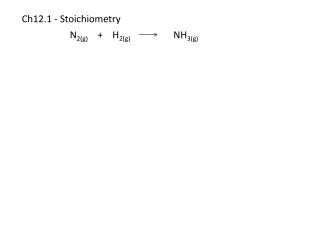
Chemistry Unit 7: Moles
160 likes | 402 Vues
Chemistry Unit 7: Moles. C8A- I will define & use the concept of a mole. C8B – I will use the mole concept to calculate the number of atoms, ions, or molecules in a sample of material. C8C – I will calculate percent composition & empirical and molecular formulas. VERY.

Chemistry Unit 7: Moles
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chemistry Unit 7: Moles C8A- I will define & use the concept of a mole.C8B – I will use the mole concept to calculate the number of atoms, ions, or molecules in a sample of material.C8C – I will calculate percent composition & empirical and molecular formulas. created by C. Johannesson modified by T. Howard
VERY A large amount!!!! • A. mole – amount of substance that has particles equal to the number of atoms in 12g of carbon 12 OR the amount of substance that has Avogadro’s # of particles --- 6.02 x 1023 particles
A. What is the Mole? HOW LARGE IS IT??? 1 mole of pennies would cover the Earth 1/4 mile deep! 1 mole of hockey pucks would equal the mass of the moon! 1 mole of basketballs would fill a bag the size of the earth!
B. Avogadro’s number – number of particles in 1 mole of a pure substance 6.02 x 1023
C. atomic mass number – number of protons + neutrons; measured in amu’s ---this is NOT on the p-table D. average atomic mass number – average weighted mass of an atom/element ---this is on the periodic table If you change the units from amu to grams you now have the amount of grams in 1 mole of the element – something you can actually measure on a scale!
avg atomic mass calculation ( % isotope #1) ( mass isotope #1) + ( % iso#2) ( mass iso#2) +… 100 C6D Use isotopic composition to calculate average atomic mass of an element.
The natural abundance for boron isotopes is: 19.9% 10B (10 amu) and 80.1% 11B (11amu). Calculate the atomic weight of boron. [(19.9 × 10) + (80.1 × 11)] 100 avg atomic mass is 10.801 amu
E. Molar mass – mass of 1 mole of a pure substance----units are grams/mole or g/mol • Turn to p.7 in your packet (Molar Mass Wkst 3)! • Look at right side of page & we will do a couple of examples…the rest is for you to complete
1. Molar mass is “equal” to the mass # of an element in amu’s, so if an element has an mass # of 39.0983 amu’s then the molar mass is 39.0983 g/mol you just change the unit of measurement!
F. formula mass aka formula weight– sum of all the mass numbers of the atoms in a compound • the term formula mass is usually associated with ionic compounds & • the term molecular mass is usually associated with covalent compounds • they’re the same basic thing
from the periodic table • #3 – BeCl2 Be = 1 x 9.012 g = 9.012 g Cl = 2 x 35.453 g = + 70.906 g 79.918 g number of atoms in the formula formula mass of BeCl2 aka molar mass
#7 – Mg(OH)2 Mg = 1 x 24.305 = 24.305 g O = 2 x 15.999 = 31.998 g H = 2 x 1.008 = 2.016 g f.m. of Mg(OH)2 = 58.319 g You need to do the rest on your own!
G. percent composition- percent by mass of each element in a compound mass of element x 100 = % element in cmpd mass of total cmpd
What percent by mass of Mg(OH)2 is oxygen? • find the formula mass of the Mg(OH)2 Mg = 1 x 24.305 = 24.305 g O = 2 x 15.999 = 31.998 g H = 2 x 1.008 = 2.016 g f.m. of Mg(OH)2 = 58.319 g
mass of element x 100 = % element in cmpd mass of total cmpd 31.998g O x 100 = 54.87% oxygen by mass 58.319g Mg(OH)2 That means more than half of the mass of the Mg(OH)2 (what is the name of the compound?) is due to oxygen!
H. % error= (observed value - actual value) x 100 actual value Observed value refers to the data you got in the lab while actual value is the “correct” or “book” value/answer.