Overview of the Skeletal System: Structures, Functions, and Bone Composition
200 likes | 312 Vues
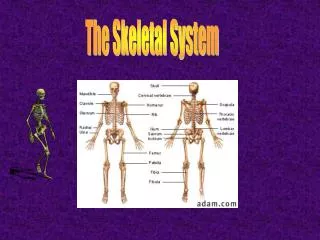
The skeletal system serves as the body's framework, protects internal organs, stores calcium, and is critical in red bone marrow formation. Bones, a form of connective tissue, are the second hardest tissue in the body, with dental enamel being the hardest. The chapter details the structure and functions of various bones, including long bones and their composition. It covers the role of bone marrow, cartilage, joints, ligaments, the synovial membrane, and synovial fluid in facilitating smooth movements and connecting bones to support a variety of motions.

Overview of the Skeletal System: Structures, Functions, and Bone Composition
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Skeletal System Chapter 3
Overview of Structures, Combining Forms,and Functions of the Skeletal System
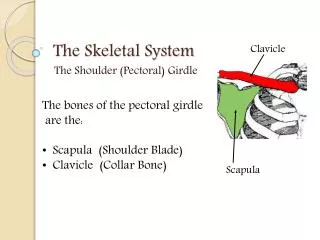
Bones • Primary Function • Act as the framework for the body • Protect the internal organs • Store the mineral calcium • Formation of red bone marrow (continues)
Structure of bones • Bone is the form of connective tissue • 2nd hardest tissue in the body • Dental enamel is #1
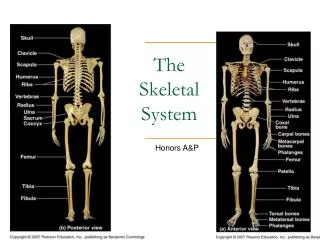
Bones • Typical Long Bone (continues)
Bones (continues)
Bones (continues)
Bones (continues)
Bones (continues)
Bones (continues)
Bone Marrow • Primary Function • Red bone marrow forms some blood cells. • Yellow bone marrow stores fat.
Cartilage • Primary Function • Creates a smooth surface for motion withinthe joints • Protects the ends of the bones
Joints • Primary Function • Work with the muscles to make a variety ofmotions possible (continues)
Ligaments • Primary Function • Connect one bone to another (continues)
Synovial Membrane • Primary Function • Forms the lining of synovial joints • Secretes synovial fluid
Synovial Fluid • Primary Function • Lubricant that makes smooth joint movementspossible