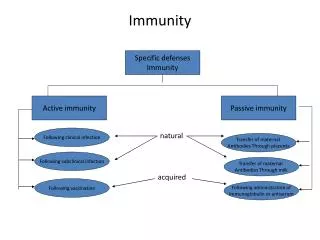
Immunity from Disease
150 likes | 311 Vues
Immunity from Disease. What is a infectious disease?. Pathogen causes A change that disrupts the homeostasis in the body. Main agents can be Bacteria Protozoans Fungi Viruses Sources can be soil contaminated water and infected animals (that includes us) . Bacteria.

Immunity from Disease
E N D
Presentation Transcript
What is a infectious disease? • Pathogen causes A change that disrupts the homeostasis in the body. Main agents can be • Bacteria • Protozoans • Fungi • Viruses Sources can be soil contaminated water and infected animals (that includes us)
Two Protozoans (and a Sponge)for 4 Flutes • The protozoans, of which there are over 30,000 species, are primitive, single-celled organisms, of which the best known example is probably the amoeba. Paramecium caudatum is one of the most common freshwater ciliates. The nasty-sounding Plasmodium virax is the malaria parasite; like many parasites it has a complex life-cycle involving several hosts, and exists in several forms. Sponges are the most primitive group of multi-cellular animals. The Bath Sponge Euspongia mollissima finds itself in this piece on the strength of it's mellow name. http://www.jsimonvanderwalt.com/catalog/plasmo.mid
Fungihttp://www.ucl.ac.uk/Pharmacology/dc-bits/fungi-pics1-04m.jpgFungihttp://www.ucl.ac.uk/Pharmacology/dc-bits/fungi-pics1-04m.jpg • http://www.microbe.org/microbes/fungi1.asp • http://waynesword.palomar.edu/ww0504.htm • http://waynesword.palomar.edu/slime1.htm • The Kingdom Fungi are important organisms, both in terms of their ecological and economic roles. • They breaking down dead organic material, • , most vascular plants could not grow without the symbiotic fungi, or mycorrhizae, that inhabit their roots and supply essential nutrients • . Other fungi provide numerous drugs (such as penicillin and other antibiotics), foods like mushrooms, truffles and morels, and the bubbles in bread, champagne, and beer.Fungi also cause a number of plant and animal diseases: • in humans, ringworm, athlete's foot, and several more serious diseases are caused by fungi. • . Plant diseases caused by fungi include rusts, smuts, and leaf, root, and stem rots, and may cause severe damage to crops.
Viruses • Made of protein coat • Are they living? • What are the criteria for life? • Don’t respire • Don’t grow • Don’t develop • CAN make copies of themselves but only with hosts help • Named after the illness or organ they infect.
From birth symbiotic relationships are established • You are “inoculated” with microorganisms on your • skin • upper respiratory system, • lower urinary and reproductive tracks • Lower intestinal track
How they help • They maintain equilibrium within the body by keeping other microorganisms from growing • Can become potential pathogens when • Conditions change and helpful organisms are eliminated • Beneficial bacteria enter areas of the body where they are not normally found • Body becomes weakened or injured
Infectious disease • Caused by the presence of pathogens • Not all diseases caused by pathogens some are • Inherited • Caused by wear and tear • Caused by exposure to chemicals (cirrhosis ) • Malnutrition (scurvy)
What do we use to figure out if it’s a pathogen? • Koch’s postulates • 1 • 2 • 3 • 4
How are Pathogens Spread • Must have continual source of the pathogen • Living - • Carriers human/ other animals • Incubation period- don’t show it yet • Dead • Inanimate object soil/ water • Fungi • botulism • Intestinal parasites from water
Transmission • Four ways • Direct contact- Cold, STD’S • By an object- money, toys, towels • Through the air- Cough, sneezes.. • By an intermediate organism (vector) • West Nile virsus- • Lyme disease- • Bubonic plague