Antibiotics Overview for Nursing
410 likes | 442 Vues
Learn about different classes of antibiotics including Penicillins, Cephalosporins, Carbapenems, and Tetracyclines. Understand their expected pharmacological actions, therapeutic uses, complications, contraindications, precautions, and nursing administration.

Antibiotics Overview for Nursing
E N D
Presentation Transcript
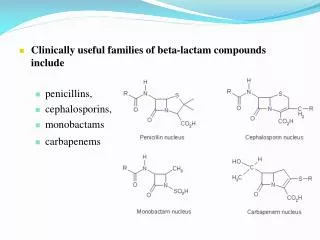
Penicillins • Penicillin G (IM) • Penicillin V (PO) • Amoxicillin • Amoxicillin-clavulanate • Nafcillin • Oxacillin • Ticarcillin • Piperacillin
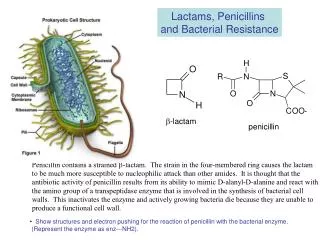
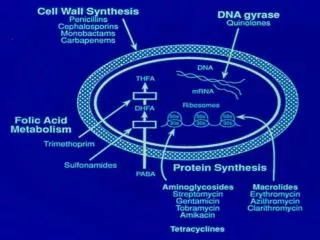
Expected pharmacological action • Destroy bacteria by weakening the bacterial cell wall • Therapeutic uses: • Treat infections due to gram-positive cocci such as streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumonia and meningitis) and streptococcus pyogenes (pharyngitis) • treat meningitis due to gram-negative cocci such as Neisseria meningitidis • Kills spirochetes, such as treponema pallidum (syphilis) • Provide prophylaxis against bacterial endocarditis in at-risk patients prior to dental and other procedures
Complications • Allergies, anaphylaxis • Kidney impairment • Hyperkalemia, hypernatremia, dysrhythmias • Contraindications/precautions • History of severe allergic reaction to penicillins and cephalosporins is a contraindication • Use cautiously in older patients, young children, and acutely ill patients • Patients who are allergic to one penicillin should not be given ANY penicillin as they are at risk for cross-sensitivity • Also, patient who are allergic to PCN are also very likel;y to be allergic to cephalosporins; do not administer
Interactions • Penicillin in the same IV solution as aminoglycosides inactivates the aminoglycoside- do not mix • Probenecid delays the excretion of penicillin • Nursing administration: • Advise patients to take penicillin preparations with food; can cause nausea and vomiting • Report any symptoms of allergic response (dyspnea, skin rash, itching, hives) • Advise patient to complete entire course of therapy • Advise female patient to use an additional form of contraception • ALWAYS assess patient for allergies!!! www.PresentationPro.com
Cephalosporins • Cephalexin • Cefazolin- IM or IV use • Cefaclor • Ceftriaxone • Cefotaxime • Cefepime • Ceftaroline www.PresentationPro.com
Expected pharmacological action • Destroy bacterial cell wall, similar to penicillins • There are 5 generations, with each subsequent generation: • More likely to reach CSF • Less susceptible to destruction by beta-lactamase • More effective against gram-negative organisms and anaerobes • Therapeutic uses: • UTIs • Post-op infections • Pelvic infections • Meningitis www.PresentationPro.com
Complications • Allergy, hypersensitivity, anaphylaxis • Possible cross-sensitivity with penicillin • Bleeding tendencies from ceftriaxone • Thrombophlebitis with IV infusion • Renal insufficiency • Pain with IM injection • Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis (C diff) www.PresentationPro.com
Contraindications/precautions and interactions • Do not give to patients with suspected or known sensitivity or allergy to penicillin • Use with caution in patients with renal insufficiency or bleeding tendencies • Intolerance to alcohol (disulfuram reaction) occurs with simultaneous use of alcohol and cefazolin • Probenecid delays renal excretion • Instruct patient to finish entire course of therapy • Advise patient to take cephalosporins with food • Instruct patient to store oral solutions in a refrigerator www.PresentationPro.com
Carbapenems • Imipenem-cilastatin • Meropenem- both for IV use (IVPB) • Expected pharmacological action: destroy bacterial cell walls • Therapeutic uses: pneumonia, peritonitis, UTI due to gram-positive cocci, gram-negative cocci, and anaerobic bacteria • Complications: • Allergy, hypersensitivity-possible cross-sensitivity to penicillin and cephalosporins • GI distress • Superinfection www.PresentationPro.com
Contraindications/precautions and interactions • Pregnancy/breastfeeding • Use cautiously in patients who have renal insufficiency • Interactions: • Imipenem-cilastatin can reduce blood levels of valproic acid with possible breakthrough seizures • Nursing administration: • Advise patients to complete entire course of therapy, even if symptoms resolve www.PresentationPro.com
Tetracyclines • Tetracycline • Doxycycline • Minocycline • Demeocycline • Expected pharmacological action: broad-spectrum antibiotics that prevent microorganism growth by preventing protein synthesis (bacteriostatic) www.PresentationPro.com
Therapeutic uses • Acne vulgaris (topical and oral) • Periodontal disease (topically) • Rickettsial infections (Rocky Mountain spotted fever, typhus fever) • Chlamydia • Brucellosis • Pneumonia due to Mycoplasma • Lyme disease • Cholera • Anthrax • H. pylori www.PresentationPro.com
Adverse effects • GI discomfort • Yellow or brown tooth discoloration • Hepatotoxicity • Photosensitivity • Superinfection • Dizziness/lightheadedness with parenteral administration www.PresentationPro.com
Contraindications/precautions and interactions • Pregnancy/breastfeeding • Use cautiously in liver and kidney disease • Interactions: • Milk products, calcium and iron supplements, antacids cause reduced absorption • Tetracycline decreases the effects of oral contraceptives • Increase risk of digoxin toxicity • Nursing administration • Take on an empty stomach with plenty of water; can take with food of gastric upset occurs • Advise to complete entire course of therapy • Advise use of an additional contraceptive www.PresentationPro.com
Macrolides • Erythromycin • Azithromycin • Clarithromycin • Expected pharmacological action: slows the growth of microorganisms by inhibiting protein synthesis; is bactericidal at high doses • Therapeutic uses: can use in patient with penicillin allergy, Legionnaires disease, pertussis, acute diptheria, chlamydia, and strep www.PresentationPro.com
Adverse effects • GI discomfort • Prolonged QT intervals • Ototoxicity with high doses • Superinfection of the bowel • Thrombophlebitis with IV administration • Contraindication: liver disease and prolonged QT syndrome www.PresentationPro.com
Interactions and nursing administration • Erythromycin inhibits the metabolism of antihistamines, theophylline, carbamezapine, warfarin and digoxin which can lead to toxicity • Nursing administration: • Except for azithromycin, administer oral preparations on an empty stomach • Instruct patient to complete entire course of therapy • Carefully monitor the PT/INR of patients on warfarin • Monitor LFTs f patients on therapy longer than 2 weeks www.PresentationPro.com
Aminoglycosides • Gentamycin • Vancomycin • Tobramycin • Neomycin • Streptomycin • Paromycin • Expected pharmacological action: destroy microorganisms by disrupting protein synthesis www.PresentationPro.com
Therapeutic uses • Gram-negative bacilli such as E. cloi, Klebsiella, proteus, psudomonas • Paromycin can be used for intestinal infections ans tapeworm infestations • Oral neomycin suppresses the normal GI flora pre-op • Streptomycin can treat TB infections in conjunction with other Abs • Adverse effects: • Ototoxicity • Nephrotoxicity • Respiiratory depression • Hypersensitivity • Peripheral neuritis www.PresentationPro.com
Contraindications/precautions • Use cautiously in patients with hearing loss or renal insufficiency; these patients should receive low doses • Interactions: • Penicillin can possibly inactivate aminoglycosides • Concurrent use of other ototoxic meds such as loop diuretics increases the risk of hearing loss • Nursing administration: • Most aminoglycosides are given parenterally • Effectiveness is measured in peak and trough levels www.PresentationPro.com
Antimycobacterial (selective antituberculosis) • Pyrazinimide • Ethambutol • Rifapentine • Isoniazid • Expected pharmacological action: highly specific for mycobacteria; prevents synthesis of mycolic acid in the cell wall • Therapeutic uses: latent and active tuberculosis; meds are given once daily for 9 months www.PresentationPro.com
Complications, contraindications and precautions • Peripheral neuropathy • Hepatotoxicity • Patients with liver disease should not take isoniazid • Interactions: can lead to phenytoin toxicity; concurrent use of tyramine-containing foods, alcohol increases the risk for hepatotoxicity • Nursing administration: meds are usually taken PO or IM; direct observation can increase adherence in active illness; take on empty stomach but can take with food if gastric upset occurs; patient must complete course of therapy www.PresentationPro.com
Broad-spectrum antimycobacterial- rifampin • Expected pharmacological action: inhibits protein synthesis • Therapeutic uses: effective for gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, part of combination therapy to treat tuberculosis • Complications: • Orange-brown discoloration of body fluids (urine, saliva, sweat and tears) • Hepatotoxicity • Mild GI discomfort • Pseeudomembranous colitis (C. diff) • Use cautiously in patients who have liver dysfunction www.PresentationPro.com
Interactions and nursing administration • Diminishes the effects of warfarin, oral contraceptives, and HIV meds • Concurrent use with isoniazid causes increased risk of hepatotoxicity • Administer orally or via IV • Give on empty stomach • Advise female client to use an additional form of contraception www.PresentationPro.com
Antiprotozoal- metronidazole • Expected pharmacological action: broad-spectrum antimicrobial with bactericidal activity against anaerobic microorganisms • Therapeutic uses: treatment of trichomoniasis, intestinal amebiasis, prophylactic use in pre-op patients at high risk for infection • Complications: • GI discomfort • Darkening of urine • Neurotoxicity and CNS effects • Superinfection www.PresentationPro.com
Antiprotozoal • Contraindicated in pregnancy and breastfeeding • Alcohol causes facial flushing, vomiting, dyspnea, and tachycardia • Affects action of warfarin, phenytoin, and lithium • Administer via IV or orally • Complete entire course of therapy • If treating trichomoniasis, treat sexual partner also www.PresentationPro.com
Antifungals • Amphotericin B • Ketoconazole • Nystatin • Miconazole • Clotrimazole • Fluconazole • Acts on fungal cell membranes to act as a fungicidal or fungistatic • Treat superficial (nails, skin and mucous membranes) and systemic fungal infections www.PresentationPro.com
Complications • Infusion reactions • Thrombophlebitis • Nephrotoxicity • Electrolyte imbalance • Bone marrow suppression • Hepatotoxicity • Gynecomastia • Irregular menstrual flow www.PresentationPro.com
Contraindications, precautions and interactions • Use cautiously in patients with renal impairment, anemia • Pregnancy/lactation • Aminoglycosides have an increased nephrotoxic risk • Digoxin, warfarin, sulfonylureas: increase levels of these meds • Amphotericin B is highly toxic and should be reserved for life-threatening infections www.PresentationPro.com
Nonopioid analgesics • Aspirin • Ibuprofen • Naproxen • Indomethacin • Diclofenac • Ketorolac • Meloxicam • Celecoxib www.PresentationPro.com
Expected pharmacological action • Use results in reduced inflammation, fever and pain • Therapeutic uses: • Inflammation suppression • Mild-moderate pain • Fever reduction • Dysmenorrhea • Aspirin: above uses, plus inhibition of platelet aggregation, protecting against stroke and MI www.PresentationPro.com
Complications • GI distress • Impaired kidney function • Celecoxib: increased risk of MI, stroke • Aspirin: Reye syndrome • CNS effects: confusion, drowsiness, nausea • Headache • Sweating, flushing • Tachycardia • Tachypnea • Aspirin toxicity www.PresentationPro.com
Contraindications/precautions • Pregnancy • Peptic ulcer disease • Bleeding disorders • Hypersensitivity • Advanced kidney disease • Celecoxib: do not use in cardiac disease www.PresentationPro.com
Interactions • Anticoagulants increase the risk of bleeding • Glucocorticoids increase the risk of gastric bleeding • Alcohol increases the risk of bleeding • Ibuprofen decreases the effects of low-dose aspirin • There are many interactions with other OTC meds • Advise patient to stop aspirin 1 week prior to surgery • Do not crush or chew enteric-coated tablets report gastric discomfort www.PresentationPro.com
Acetaminophen • Expected pharmacological action: slows the production of prostaglandins in the CNS • Analgesic and Antipyretic effects • Acute toxicity: results in liver damage • Administer the antidote, acetylcysteine • Contraindicated in those who have three or more alcoholic drinks per day-increases the risk of liver damage • Can lead to increased levels of warfarin • The FDA recommends only taking one form of acetaminophen at a time www.PresentationPro.com
Opioid agonists • Morphine- oral, sub-q, IM, IV, epidural, intrathecal • Fentanyl- IV, IM, transdermal • Meperidine- oral, IM, IV, sub-q • Codeine- oral, sub-q, IM, IV • Methadone- oral, sub-q, IM • Oxycodone- oral, rectal • Hydromorphone- oral, sub-q, IM, IV • Act on mu receptors in CNS to produce analgesia, respiratory depression, euphoria, and sedation; also decreased GI motility www.PresentationPro.com
Complications • Respiratory depression • Constipation • Orthostatic hypotension • Urinary retention • Cough suppression • Sedation • Biliary colic (gallbladder pain) • Nausea, vomiting • Coma, pinpoint pupils, respiratory depression (overdose) www.PresentationPro.com
Contraindications/precautions • Do not use in biliary surgery (morphine) • Do not use prenatally in premature delivery • Do not use meperidine in renal failure • Use with caution in the following patients: • Asthma • Pregnancy • Labor • Inflammatory bowel disease • Enlarged prostate • Hepatic or renal disease www.PresentationPro.com
Interactions • CNS depressants have additive CNS effects • Anticholinergic agents: increased effects • Antihypertensives can have additive hypotensive effects • Assess pain levels and vital signs frequently • Follow controlled-substance procedures • Have naloxone and resuscitation equipment available • For cancer patients, give on a fixed schedule • Advise about physical dependence • The first dose of a transdermal fentanyl patch will take several hours to take effect www.PresentationPro.com
Opioid agonists-antagonists • Butorphanol- IM, IV, intranasal • Nalbupine- IM, IV, sub-q • Buprenorphine- IV, sublingual, transdermal • Pentazocine- IV, IM, sub-q • Have same actions, complications, contraindications and interactions as opioid agonists with less sedative and addictive effects www.PresentationPro.com
Opioid antagonists • Naloxone- IV, IM, sub-q, intranasal • Naltrexone- oral, IM • Interfere with the action of opioids by competing for opioid receptors (mu receptors) • Used to reverse effects of opioids • Can cause tachycardia, tachypnea, cramping, hypertension, vomiting • Has rapid action • Two or more doses may be needed-has shorter half-life than most opioids www.PresentationPro.com