Photosynthesis
70 likes | 174 Vues
Understand the process of photosynthesis and the structure of plant leaves. Learn how plants convert sunlight into sugars, the role of chloroplasts, and the exchange of gases in stomata. Dive into the details of this vital process and leaf anatomy.

Photosynthesis
E N D
Presentation Transcript
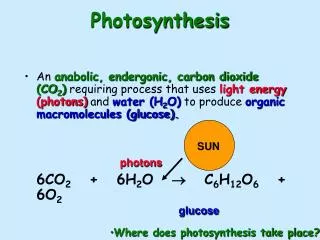
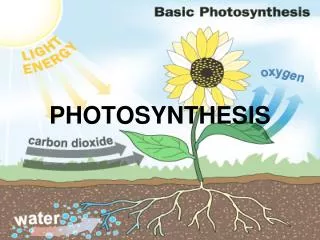
I. Photosynthesis in Overview • Process by which plants and other autotrophs turn the energy of sunlight into sugars. Requires sunlight, water, and carbondioxide. • Overall equation:6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Light C6H12O6 + 6 O2 • Occurs in the leaves of plants in organelles called chloroplasts.
Stoma Mesophyll Cell Chloroplast II. Plant Leaf Structure • Basic Leaf Structure • Stomata (Stoma) • Mesophyll Cell • Chloroplasts
Oxygen (O2) Carbon Dioxide (CO2) II. Plant Leaf Structure • B. Basic Leaf Structure • Stomata (Stoma)are pores in a plant leaf surface through which water and gases are exchanged between the plant and the atmosphere.
Nucleus CellWall Chloroplast Central Vacuole II. Plant Leaf Structure • Basic Leaf Structure • 2. The mesophyll cell is a cell found on the surface of a leaf.
II. Plant Leaf Structure • Basic Leaf Structure • 3. Chloroplasts are tiny organelles within the plant cell where photosynthesis takes place.
III. Photosynthetic Process • Plants take in carbondioxide (CO2) • Plants take in water (H2O) • Plants absorb light (Light) • Sugar (plant food) is created (C6H12O6) • Oxygen is produced and released (O2) • 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + Light C6H12O6 + 6 O2