Anglo-Saxon England
190 likes | 459 Vues
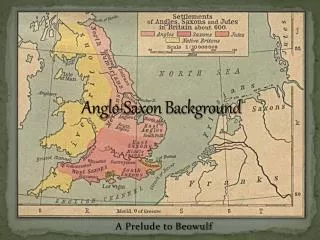
Anglo-Saxon England. The Origins of Beowulf. So Who Were the Anglo-Saxons?. Germanic tribes from central Europe The Angles, the Saxons, and the Jutes Moved east and eventually into England around 450 C.E. Conquered by 800 C.E. through fighting process Successful groups absorbed the losers.

Anglo-Saxon England
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Anglo-Saxon England The Origins of Beowulf
So Who Were the Anglo-Saxons? • Germanic tribes from central Europe • The Angles, the Saxons, and the Jutes • Moved east and eventually into England around 450 C.E. • Conquered by 800 C.E. through fighting process • Successful groups absorbed the losers
Warrior Culture • Kinship • The individual ceases to exist, responsible for all behavior of family members • Lordship • The king is tied to everyone • Pursues interest of all members • Selfless- Kinship • Military relationship • King is tied to the nobles who provide the soldiers who fight for the king
Elements of the Warrior Culture • Wergild = the man price • When you offend a family you must offer compensation • Provides peace without causing a feud • If you murder a man outside of war, usually there was an execution • Repairs evil done by death
Warrior Culture Continued • Lof = esteem, reputation • Warrior wants story told over and over so legacy and fame will live on • Immortality in the eyes of men! • Wyrd = fate • Destiny of the warrior
The Epic Poem • The Oral Tradition • Stories passed down by telling them • Usually told by a bard who sings • Long narrative with heroic theme • Story of the hero’s journey • In the 3rd person • Contains information about the culture that created them • Contains clues as to what people feared • Examples: The Odyssey, The Iliad • Beowulf dates back to some time between 700- 1000 CE
Old English • This is the language of Beowulf, also known as Anglo-Saxon • Many people confuse Shakespearean language as Old English • It is actually Modern English • Shift to Modern English did not occur right away • Took hundreds of years
Old English Continued • Uses unfamiliar letters that come from runic alphabet of Germanic peoples • Despite the fact that it looks so different, once you know what the sounds the letters make it sounds very similar to English • For example: • “Pætwæs god cyning!” • The P makes a th sound