Glaciers
140 likes | 436 Vues
Glaciers. By: Naomi Cary & Elizabeth Baldwin. What are glaciers?.

Glaciers
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Glaciers By: Naomi Cary & Elizabeth Baldwin
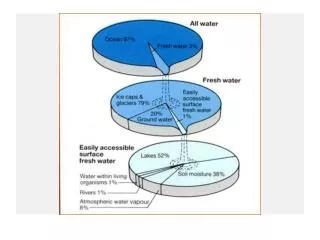
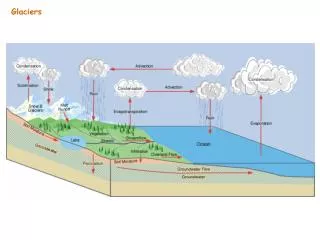
What are glaciers? • Glaciers are enormous masses of moving ice. Glaciers are heavy and are capable of moving across the Earth’s surface. They erode, move, and deposit large quantities of materials. Glaciers form in areas that are very cold and have snow year round. These usually form in polar regions.
Alpine Glaciers • Alpine glaciers form in mountainous areas. There is one common type of alpine glaciers; valley glaciers. • Valley glaciers are formed by stream erosion. • These glaciers flow downhill slowly, and widening the valleys into U-shaped valleys.
Continental Glaciers • Continental glaciers are huge continuous masses of ice. • The largest type of a continental glacier is a continental ice sheet. • These ice sheets can cover millions of square kilometers with ice.
Icebergs • Icebergs are large pieces of ice that break off of ice shelves and drift into the oceans. • Icebergs form by a process called calving. • Icebergs are hazards for ships because they cannot see how far the icebergs extends.
Crevasses • Crevasses occur when glaciers flow forward. • Crevasses are large cracks that form where the glacier picks up speed or flows over a high point. • These cracks happen because the ice cannot stretch quickly. • These can be very dangerous for people who are traveling across glaciers because a bridge layer of snow can hide these cracks from view.
Landforms • Alpine glaciers carve out rugged features in the mountain rocks through which they flow. • Continental glaciers smooth the landscape by scraping and removing features that existed before the ice appeared.
Glacial Drift • Glacial drift is all the material carried and deposited by glaciers. • There are two main types, stratified drift and till deposits. • This is based on whether the material is sorted or unsorted.
Stratified drift • Stratified drift happens when rock material that has been sorted and deposited in layers by water flowing from the melted ice. • Many streams are created from the melting water of a glacier. • The streams carry a lot of sorted material, which is later deposited in front of the glacier.
Till Deposits • Till is unsorted rock material that is deposited directly by the ice when it melts. • The till is made up of different sizes of rock material. • The most common till deposits are moraines. • Moraines generally form ridges along the edges of glaciers. • They are produced when glaciers carry material to the front of the ice and along the sides.
Summary • Glaciers are large masses of ice that move across the world. There are two types of glaciers; Alpine and Continental. • Alpine glaciers create; horns, cirques, arêtes, u-shaped valleys, and hanging valleys. Continental glaciers create; ice shelves, icebergs, and crevasses. • Glaciers carry material and deposits. There are two types of glacial drift; stratified drift and till deposits.