Cell Reproduction “Mitosis”
110 likes | 234 Vues
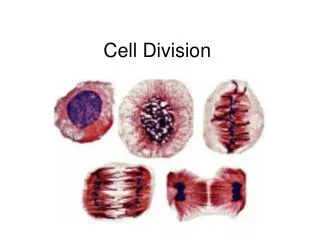
Mitosis is a fundamental process of somatic (body) cell division essential for growth, maintenance, and asexual reproduction. The cell life cycle consists of interphase and mitotic phases. In interphase, the cell undergoes G1 (growth), S (DNA replication), and G2 (preparation for division). During mitosis, the cell divides into two identical daughter cells through four stages: Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase (PMAT). Cytokinesis occurs afterward, creating distinct daughter cells in both plant and animal cells. Understanding mitosis is crucial for studying cellular functions and development.

Cell Reproduction “Mitosis”
E N D
Presentation Transcript
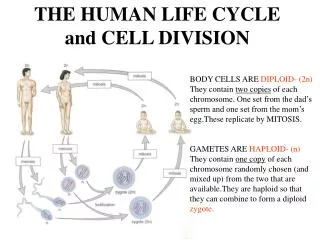
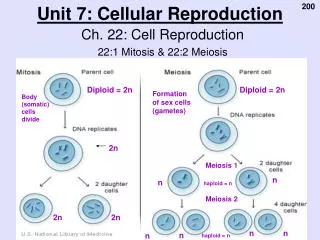
Somatic (Body) Cell Life Cycle(everything but eggs and sperm) • INTERPHASE (Everything ‘in between’ mitotic cell divisions.) • G1: Newly formed cell grows up and does its job. • S Phase: Cell starts copying its DNA • G2: The cell continues to do its regular job, but more slowly and important organelles are duplicated. • MITOSIS • Cell divides into two identical daughter cells. • Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase
MITOSIS • Asexual reproduction of cells. • Also called cloning and vegetative propagation. • Results in two, identical daughter cells. • Necessary for: • Maintenance • Growth • Reproduction in asexual species
PMAT 4N Cell • PROPHASE • Condensed chromosomes • Bye bye nuclear envelope • Centrioles hook spindle fibers to chromosomes
PMAT 4N Cell • METAPHASE • Chromosomes line up at the plate. Sister Chromatids Homologous Chromosomes
4N Cell PMAT • ANAPHASE • Spindle fibers pull sister chromatids apart toward centrosomes.
PMAT 2, 2N Cells • TELOPHASE • Hello nuclear envelope! • Good bye spindle fibers! • Chromosomes decondense (is this a word?) • Cell plate forms in plants/ cell membrane pinches off in animals.
Cytokinesis • PLANTS: • Cell wall forms between new cells • ANIMALS: • New plasma, or cell membrane forms around new cells.