Situational Leadership
290 likes | 1.31k Vues
Situational Leadership. Dr. Ed Merritt California State University (Cal Poly Pomona) eamerritt@csupomona.edu. Learning Objectives. At the end of this session you will be able to— Explain the four types of situational leadership Define your preferred leadership style

Situational Leadership
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Situational Leadership Dr. Ed Merritt California State University (Cal Poly Pomona) eamerritt@csupomona.edu
Learning Objectives At the end of this session you will be able to— • Explain the four types of situational leadership • Define your preferred leadership style • Choose and apply the appropriate leadership style to a managerial situation at the club Business Management Institute
Consider Implementing an action plan when you return-- • Take-home points • Points for action at your club • People with whom to communicate the value of this knowledge Business Management Institute
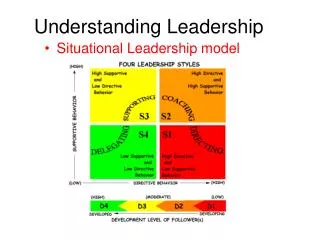
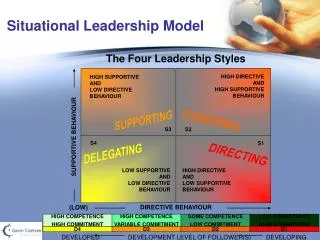
Background Blanchard and Hersey characterized leadership style in terms of the amount of direction and support that the leader gives to his or her followers: • Directing • Coaching • Supporting • Delegating (details to follow) Business Management Institute
Situational Leadership Exercise • Defining your preferred style • Spend 10 minutes • Answer 12 statements • Score your preferred style • We will review in class Business Management Institute
Directing Leaders define the tasks and supervise them closely • Decisions are made by the leader • Communication is largely one-way • Also referred to as autocratic, militaristic Business Management Institute
Coaching Leaders still define tasks, but seek ideas and suggestions • Decisions remain the leader's prerogative • Communication is much more two-way • Also referred to as consultative Business Management Institute
Supporting Leaders pass day-to-day decisions to employees • Leader facilitates but control is with the employees • Also referred to as participative or democratic Business Management Institute
Delegating Leaders involved in decisions and problem-solving • Control is with the employee • Employee decides how leader will be involved • Also referred to as laissez-faire Business Management Institute
Application Effective leaders are versatile • Changing style according to the situation • No one right style • We tend to have a preferred style, and in applying Situational Leadership you need to know which style to use Business Management Institute
Employee has: Low confidence Low commitment Generally lacking the specific skills required for the job Leader uses: Directing behavior Application: Directing Example: Entry level employee who does not know how to set a table Business Management Institute
Employee has: Some competence Low commitment May have some relevant skills, but won't be able to do the job without help Leader uses: Coaching behavior Application: Coaching Example: Established a la carte server who may be working a large reception for the first time Business Management Institute
Employee has: High confidence Variable commitment Experienced and capable, but may lack the confidence to go it alone Leader uses: Supporting behavior Application: Supporting Example: An experienced club reception supervisor who is reluctant to accept the reception desk manager position Business Management Institute
Employee has: High competence High ability Experienced at the job, and comfortable with own ability to do it well Leader uses: Delegating behavior Application: Delegating Example: Experienced director of golf at a country club. Director is more skilled in area than GM Business Management Institute
Action Plan • What are some take-home points? • What are some points for action at your club? • How and to whom will you communicate the value of this knowledge? Business Management Institute
Situational Leadership Dr. Ed Merritt California State University (Cal Poly Pomona) eamerritt@csupomona.edu