Using Stem Cells
110 likes | 287 Vues
Stem cells are unique cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation into various tissues, holding potential for medical advancements. There are two major types: embryonic stem cells from blastocysts and adult stem cells found in various tissues. Stem cell research is crucial for understanding organism development, testing drugs, and treating diseases like Parkinson’s and leukemia. However, the use of embryonic stem cells raises ethical questions regarding the moral status of embryos. This article explores the advantages, disadvantages, and implications of stem cell research.

Using Stem Cells
E N D
Presentation Transcript
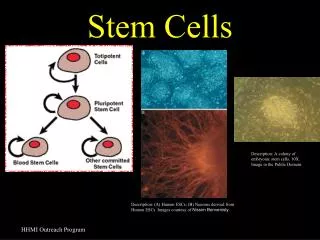
Using Stem Cells • A stem cellis a cell that can continuously divide and differentiate into various tissues. • Some stem cells have more potential to differentiate than others. • Adults’ bodies have some multipotent cells that can be removed, frozen or cultured, and used for medical treatments. • The cells of new embryos have more potential uses. • The use of embryos for stem cell research poses ethical problems. • An alternative source of embryonic stem cells is through SCNT (somatic cell nuclear transplant).
What are Stem Cells? Stem Cells are extraordinary because: They can divide and make identical copies of themselves over and over again (Self-Renewal) Remain Unspecialized with no ‘specific’ function or become . . . . Specialized (Differentiated) w/ the potential to produce over200different types of cells in the body.
The Major Types of Stem Cells • Embryonic Stem Cells • From blastocysts left over from In-Vitro Fertilization in the laboratory • From abortedfetuses • B. Adult Stem Cells • Stem cells have been found in the blood, bone marrow, liver, kidney, cornea, dental pulp, umbilicalcord, brain, skin, muscle, salivary gland . . . .
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Image:Stem_cells_diagram.pnghttp://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/Image:Stem_cells_diagram.png
Advantages and Disadvantages to Embryonic and Adult Stem Cells.
http://www.pbs.org/newshour/bb/science/jan-june14/stemcells_01-29.htmlhttp://www.pbs.org/newshour/bb/science/jan-june14/stemcells_01-29.html Reprinted with permission of Do No Harm. Click on image for link to website.
Why is Stem Cell Research So Important to All of Us? • Stem cells allow us to study how organisms grow and develop over time. • Stem cells can replace diseased or damaged cells that can not heal or renew themselves. • We can test different substances (drugs and chemicals) on stem cells. • We can get a better understanding of our “genetic machinery.”
What Human Diseases are Currently Being Treated with Stem Cells? • Parkinson’s Disease • Leukemia (Bone Marrow Transplants) • Skin Grafts resulting from severe burns Stem Cell Therapy has the Potential to: • Regenerate tissues/organs • Cure diseases like diabetes, multiple sclerosis, etc.
Why the Controversy Over Stem cells? • Embryonic Stem cells are derived from extra blastocysts that would otherwise be discarded following IVF. • Extracting stem cells destroys the developing blastocyst (embryo). -Questions for Consideration- Is an embryo a person? Is it morally acceptable to use embryos for research? When do we become “human beings?”
Key ConceptQuestions • How are transgenic organisms useful to human beings? • Genetic engineering has spurred the growth of biotechnology, a newindustry that is changing the way we interact with the living world • How are cloning and stem cell research related? • Cloning can produce organisms that are geneticallyidenticalto preexisting individuals. Stem cells can be used to grow new tissues.