Understanding Transmission Lines: Key Concepts and Questions Explained
190 likes | 317 Vues
This presentation aims to demystify transmission lines for beginners. By the end, you will have a solid grasp of key concepts such as reflection coefficient, voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR), and the importance of matching. We will also cover standing waves, power loss at different VSWR levels, the significance of 50 ohms, and velocity factor. Prepare to explore the fundamental principles behind characteristic impedance and the behavior of transmission lines under various terminations. Join us to unravel the complexities of RF transmission!

Understanding Transmission Lines: Key Concepts and Questions Explained
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Transmission Lines for the Terrified Jeff9V1AS Filename:BB249_70
Hopefully, by the end of this talk, you will be able to answer the questions:1. "What is reflection coefficient?" 2. "What is VSWR" 3. "What is matching?" 4. "What are standing waves?" 5. "How much of my transmitted power is going out when my VSWR is 2?" 6. “What happens if the XYL keys up the 300W Linear while I am adjusting the spacers on the open wire feeder?”7. Why 50 ohms?8. Explain velocity factor Jeff9V1AS
What is characteristic impedance? Jeff9V1AS
Yes, I can see your formulae, but I still can’t grasp the concept of characteristic impedance! OK, let’s try again Jeff9V1AS
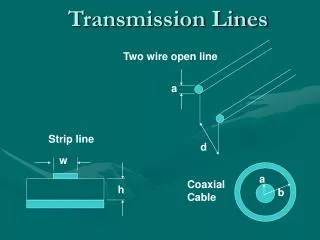
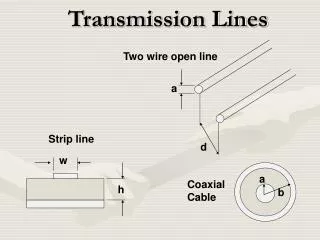
Characteristic Impedance Formulae for common transmission line types Jeff9V1AS
Why 50 ohms? Jeff9V1AS
Why 50 ohms? Jeff9V1AS
Why 50 ohms? Jeff9V1AS
Transmission and reflection Jeff9V1AS
What happens to the voltage and current for various terminations. Jeff9V1AS
V and I distribution for the special cases of ¼ and ½ lambda Jeff9V1AS
Lumped equivalents for TLs just less, equal, greater than ¼ lambda Jeff9V1AS
Different lengths can behave like different lumped circuits! What’s the catch?..... Jeff9V1AS
"This is the last time you're coming home late from your ham radio club meeting"! Jeff9V1AS