Computer Terminologies (1)
600 likes | 1.37k Vues
Computer Terminologies (1). CPU - C entral P rocessing U nit RAM - R andom A ccess M emory ROM - R ead- O nly M emory CD-ROM drive Floppy disk drive Hard disk drive Bus. Computer Terminologies (2). System unit Motherboard (Mainboard) Expansion slot Network Card Video Card

Computer Terminologies (1)
E N D
Presentation Transcript
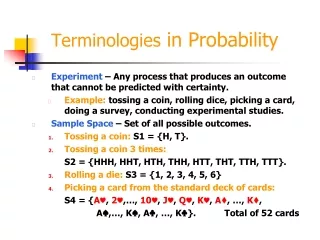
Computer Terminologies (1) • CPU - Central Processing Unit • RAM - Random Access Memory • ROM - Read-Only Memory • CD-ROM drive • Floppy disk drive • Hard disk drive • Bus
Computer Terminologies (2) • System unit • Motherboard (Mainboard) • Expansion slot • Network Card • Video Card • Sound Card • Parallel port and Serial port
Network Interface Cards • communicate through a serial connection • Each card requires an IRQ, an I/O address, and an upper memory address to work with DOS/WIN95. • To configure TCP/IP LAN settings in a Windows machine, use the Control Panel icon, Network.
Network Interface Cards • Considerations: • type of network (Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI) • type of media (CAT5, fiber, wireless) • type of system bus either PCI/ISA or PCMCIA, which is used on laptops) • To change a PCs network speed from 10Mbps to 100Mbps, you need to upgrade the NIC.
NIC: Network Interface Card • IRQ • I/O address • Memory address PCMCIA Personal Computer Memory Card International Association
Select a NIC • Type of Network: • Ethernet, Token Ring, FDDI • Type of media: • Twisted-pair, Coaxial, Fiber-optic cable • Type of system bus: • PCI, ISA
Information stored in computers • Symbols or "bits", are 1 and 0.
Computer systems only understand “on” and “off” or “1s” and “0s.” Computer systems use a binary numbering system rather than decimal. Decimal numbering system uses 10 symbols; they are 0-9. Computer systems use a Base 2 system. Binary Number System 8 bits = 1 byte A bit is a binary digit used in the binary numbering system, either 0 or 1.
Binary Number System (1, 128) =128+ (0, 64) = 0+ (0, 32) = 0+ (1, 16) =16 + (0, 8) =0+ (0, 4) =0+ (0, 2) =0+ (1, 1) =1= 145
Preparation for LAB • 1: Installation of NIC • 2: Configuring network settings