RNA Silencing RNAi
720 likes | 1.61k Vues
RNA Silencing RNAi. Post transcriptional gene regulation by siRNA and miRNA Pete Burrows MIC 759 October 26, 2006. Small untranslated regulatory RNAs Eukaryotes ncRNA Prokaryotes sRNA. Guillier, et al. Genes and Development 20:2338, 2006. Number of Publications.

RNA Silencing RNAi
E N D
Presentation Transcript
RNA SilencingRNAi Post transcriptional gene regulation by siRNA and miRNA Pete Burrows MIC 759 October 26, 2006
Small untranslated regulatory RNAs Eukaryotes ncRNA Prokaryotes sRNA
Number of Publications Entrez PubMed Search Terms: RNAi or siRNA or miRNA
Lecture Outline • Discovery • General features • siRNA • Role of translation • miRNA • Problems
Focus on RNA interference - A user’s guide September 2006 Nature Genetics June 2006 Supplement
391:806, 1998 No RNA No probe dsRNA anti-sense ssRNA In situ hybridization for mex-3 mRNA 4 cell embryos
News and Views Nature 391:744 1998
In vitro transcription Restriction digest Blunt end 5’ overhang 3’ overhang
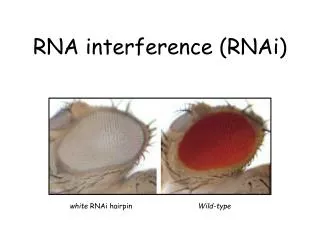
RNAiDicing and slicing • RNA silencing pathways are triggered by 21-27 nt long small RNAs • Small interfering RNAs – siRNA • Repeat-associated small interfering RNAs –rasi RNAs • Micro RNAs – miRNA • Piwi-interacting RNA - piRNA • RNAi induction using long dsRNA only operates in plants and invertebrates • Worms – soak them in a solution of dsRNA, feed them bacteria expressing the appropriate construct • In vertebrates, long dsRNA (>30 bp) induces on the IFN response including PKR, inhibits translation, and activation of RNase L, degrades mRNA
Dicer • Dicer generates RNAs with 2 nt 3’ overhang and 5’ phosphorylated terminus, both required for activity • Fly Dicer requires ATP, human may not
RISC • RISC has helicase, exonuclease, endonucelase and homology searching proteins. • Initial RISC is inactive until transformed into active form by unwinding of the siRNA duplex and loss of sense (passenger) strand • Antisense (guide) strand defines specificity of RNAi
Processing of siRNA • Starting with dsRNA • Which becomes guide strand in the RISC and which (passenger strand) is excluded? • Sequence and structure • Strand with the less-tightly base pared 5’ end is incorporated becomes guide strand • What is the endonuclease (Slicer) in RISC?
The ago1 mutant Arabidopsis develops abnormally because it does not produce an effector of silencing. The Argonaute genes were so named because the mutant plants look like an argonaute squid. Knew that Ago a RISC component The Sainsbury LaboratoryJohn Innes CentreColney LaneNorwich, NR4 7UH, UK
Identification of Argonaute 2 as Slicer in humans J. Liu et al., Science 305, 1437 -1441 (2004) Published by AAAS
Fig. 2. Argonaute2 is essential for mouse development J. Liu et al., Science 305, 1437 -1441 (2004) Published by AAAS
Fig. 3. Argonaute2 is essential for RNAi in MEFs J. Liu et al., Science 305, 1437 -1441 (2004) Published by AAAS
Sontheimer and Carthew, Science 2004 Sep 3;305(5689):1409-10
Cytosolic players in siRNA and miRNA • Dicer (DCR) • Multi domain RNase III enzyme the cleaves dsRNA or stem-loop pre-miRNA into siRNA and miRNA • TRBP • TAR RNA Binding Protein, Cofactor for Dicer • RISC • RNA induced silencing complex • Argonaute (AGO) • PAZ domain binds the characteristic two-base 3' overhangs of siRNAs • PIWI domain: dsRNA guided hydrolysis of ssRNA • Ago2 is slicer in mammalian RISC • Other Ago may function in miRNA silencing
Taphrina S. pombe S. cerevisiae Morel Penicillium http://www.glocalbeer.dkhttp://tolweb.org/tree?group=Ascomycota&contgroup=Fungi Swahili word for beer (Pombe) Schizosaccharomyces pombe has DCR and AGO but not in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Ferritin IRE-IRP Shen, et al. Differentiation 73:287-293 2005
siRNA siRNA ----Control---- -------IRE------- Fe + - + - + - + -
7:633, 2005 7:719, 2005
Colocalzation of Ago2 (Slicer) and Dcp1a (Decapping enzyme) in P-bodies
RCK human homolog of yeast Dhh 1p Interacts with eIF4e and represses translation Targets RNA to P-bodies? Sen and Blau, The FASEB Journal, 2006 20:1293
RNAi The Movie Nature Genetics 2006
miRNA • The miRNA are endogenous small RNA guides that repress the expression of target genes. • Differ from siRNA in biogenesis not in functions, although mechanisms can be different. mRNA cleavage when complementarity is extensive, repress translation when not. • lin-4 mutant worms had defects in timing of cell division. Encodes a small RNA that binds to and silenced lin-14 message. • Lin-14 mRNA levels do not decline, but that may not always be the case. • let-7 also found in other species.
miRNA • Abundant ssRNA from a few thousand to 40,000 molecules /cell • Found in all metazoans • 0.5-1% of genes • siRNA targets genes from which it is derived in a sequence specific manner • miRNA regulate separate genes and has imperfect complementarity • May be 100’s mRNA regulated by one miRNA • Usually have many binding sites in each 3’ UTR, and several different miRNA can target same 3’ region. Combinatorial control
miRNA • Many miRNA are embedded in introns of protein encoding genes and are transcribed together with host genes. • miRNA can be expressed in developmentally tissue specific fashion but may not be expressed in tissues where putative target sequences are.
The structure of human pri-miRNAs Du, T. et al. Development 2005;132:4645-4652
Processing of miRNA • Long primary Pol II transcript (pri-miRNA) • Cleaved by Drosha, nuclear RNase III endonuclease to establish one end of the miRNA (pre-miRNA) • Also need dsRNA binding protein Pasha (flies) DGCR8 (humans) • The pre-miRNA exported from the nucleus by Exportin 5 • Cut by Dicer→ miRNA • Strand with the less-tightly base pared 5’ end becomes mature miRNA, other strand becomes miRNA* and degraded • Worms and mammals only one Dicer and it makes miRNA and siRNA. Flies have one for each.
Players in miRNA biogenesis • Drosha • Nuclear RNase III enzyme. Initiates miRAN biogenesis by cleaving pri-miRNA into pre-miRNA • Pasha • Partner of drosha is a dsRNA binding protein. Human DGCR8 • Exportin-5 • Nuclear transmembrane protein that transports pre-miRNA form nucleus to cytoplasm. Works in conjunction with GTP-Ran
The miRNA biogenesis pathway Du, T. et al. Development 2005;132:4645-4652
Mechanism of miRNA suppression of gene expression • Transcription • mRNA degradation • Translational repression • 1 Initiation • 2 Elongation • 3 Termination • 4 Release • Co-translational degradation of the nascent peptide

![RNA interference (RNAi) [aka post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS)]](https://cdn4.slideserve.com/584681/rna-interference-rnai-aka-post-transcriptional-dt.jpg)