China: Land, People, and Regions
380 likes | 501 Vues
Explore China's diverse geography and culture with 1.3 billion people living in a land of rugged mountains and arable fields. Discover the ethnic groups, major regions like the Heartland, North and South China, and regions like Xinjiang and Xizang.

China: Land, People, and Regions
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Land & People • 1.3 billion people live in China • They are packed into Eastern China • Why? • 80% of the land is rugged and mountainous • 20% of the land is flat • 1/2 of the land is arable, good for farming • Most people still farmers • Many natural barriers: plateaus, deserts, mountains
The People • 92% of the people in China are ethnic Chinese or Han • Other ethnic groups live in remote regions • Mongols • Tibetans • Uyghur • Mandarin is the official government language, 1000s dialects
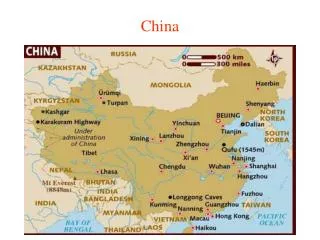
Regions of China • 6 major Regions • The Heartland – North & South • From Beijing in the north to the border with Vietnam • The Northeast – Manchuria • Mongolia • Xinjiang – pronounced (sheen jee ahng) • Xizang – pronounced (shee dzahng)
Northeast Xinjiang Xizang (Tibet) China
North China • Part of Chinese Heartland • Warm or hot summers • Cold winters • Rainfall varies • Crops: wheat & millet • Cities: Beijing (capital), Tianjin: manufacturing • Rivers: Huang He or River of Sorrow or Yellow River (same river) Page 326 • Lots of people
Beijing Financial Street, the economic center of Beijing Video Urban Boom
Wangfujing Street is one of the busiest streets in Beijing, with nearly 100,000 visitors daily
South China • Part of Chinese Heartland • North and South separated by Chang River • Richer farming and industrial region than North China • Xi River Delta • Mild Humid Climate • Crops: rice, cotton, tea, and vegetables • Lots of People packed around farmlands in river valleys and lakes
Northeast • Once Manchuria • Cold Climate • Sparsely populated • Government incentives to attract people to the region • Government working to develop region’s mineral resources • oil, iron, aluminum ore, coal, lead, zinc
Mongolia • Gobi Desert: harsh climate • Hot summers and cold winters • Part independent • Try to promote irrigation and farming • Mongolian Culture Video
Hohhot, Inner Mongolia, China. A view overlooking the city square from my Hotel.
Xinjiang • Desert Basin • Oil producing region • Linked by railroads • Produce cotton and wheat with irrigation • Home to non-Chinese people
Ürümqi is the capital of Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People's Republic of China, in the northwest of the country.
Xizang • Tibet • Sits in the Himalayas • Barren and treeless farming possible in valleys • Chinese took over Tibet in 1950 • Tried to develop hydroelectric power
1. Why did Chinese call land Zhongguo? • Believed China center of civilization • Middle Kingdom • China was located too far from other countries, it was surrounded by natural boundaries and barriers • Gobi Desert, Mongolian and Tibetan Plateaus, Himalayas, and Rainforests
2. What is the Chinese heartland? • North and South China • Most people live there because it is suitable for farming
3. What are the 3 main rivers of China? • Huang He: Yellow River, River of Sorrow • Chang: Yangzi – 3rd longest • China’s 3 Gorges Dam 2012 • National Geographic 3 Gorges Dam • Xi: trade route in South • All important for trade and farming
4. What geographic feature lies between independent Mongolia and Chinese Mongolia? • Gobi Desert