Determining Wages
230 likes | 481 Vues
Determining Wages. Chapter 15. Labor & Wages. Labor – blue-collar & white-collar workers, and small business owners Wages - the price that employers pay for labor. Includes salaries as well as fringe benefits Nominal wage Real wage. General Level of Wages.

Determining Wages
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Determining Wages Chapter 15
Labor & Wages • Labor – blue-collar & white-collar workers, and small business owners • Wages- the price that employers pay for labor. Includes salaries as well as fringe benefits • Nominal wage • Real wage
General Level of Wages • Includes a wide range of different wage rates • Wages differ among nations, regions, occupations, and individuals • Also differ by gender, race, and ethnic background
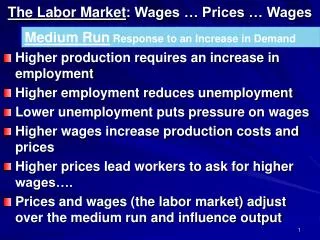
Role of Productivity • If a person is more productive, there is a greater demand for their services. • If total supply of labor remains fixed, wages will rise. • Reasons for high productivity • Plentiful capital • Access to abundant natural resources • Advanced technology • Labor quality • Intangible factors
Purely competitive labor market • Many firms compete with one another in hiring labor • Many qualified workers with identical skills supplies that type of labor • Individual firms & individual workers are “wage takers”
Market demand for labor • Firms don’t have to be in the same industry • Add the demand curves of the individual firms • Market supply- employers must pay higher wage rates to obtain more workers. They may need to bid workers away from other industries.
Labor market equilibrium • Intersection of market labor demand and market supply curves • This determines wage rate and level of employment
Monopsony model • Single employer of labor • Characteristics • Single buyer • Labor – immobile • Firm = “wage maker”
MRC Higher Than the Wage Rate • When higher wages are paid to new workers, current workers need to get paid that wage as well. • Uniform wages brings the mrc higher than the wage rate
Three Union Models • Unions bargain with a large number of employers. • Goals- better wages, hours, and working conditions for their members
Increasing Demand For Labor • Increase product demand • Increase productivity • Raise the price of other inputs
Craft Union Model • Unions can boost wage rates by reducing the supply of labor • Unions have supported legislation that has: • Restricted immigration • Reduced child labor • Encouraged compulsory retirement • Enforced a shorter workweek
Craft unions- members possess a particular skill (I.e. carpenters, electricians) • Exclusive unionism- by excluding workers from unions and from the labor supply, craft unions succeed in elevating wage rates. • Occupational licensing- laws are passed by government stating that you can practice their trade only if they meet certain requirements.
Industrial Unions • Unions seek to organize all available workers (skilled & unskilled). • Limited membership policies would make nonunion workers available to employers.
Union Wages • Union members usually get 15% higher wages over non-union
Minimum Wage • Fair Labor Standards Act (1938) allowed minimum wage and overtime • Purpose- provide a “living wage” that will allow less skilled workers to earn enough to escape poverty
Pros Increase wages without increasing unemployment May produce more jobs Increase labor productivity Reduce labor turnover Cons Less people hired Higher labor costs may force some firms out of business Better to have a job at a lower wage Minimum Wage
Marginal Revenue Productivity • Demand for labor depends on how much the worker contributes to employers revenue • Labor productivity • Demand for the products produced
Noncompeting Groups • Workers representing different occupations • Ability • Education & Training • Investment in human capital
Compensating Differences • Must be compensated for nonmonetary differences in the job • Job may be unattractive (I.e. garbage man)
Market Imperfections • Lack of job information • Geographic immobility • Unions and government restraints • Discrimination
Pay for Performance • Piece rates • Commissions • Royalties • Bonuses, stock options, profit sharing • Efficiency wages