Understanding Parallelograms: Properties, Side Lengths, and Angle Measures
120 likes | 256 Vues
This homework covers the fundamental properties of parallelograms, including the congruence of opposite sides and angles, as well as the supplementary nature of consecutive angles. Examples include finding side lengths and angle measures in specific parallelograms like FGHJ and PQRS. Additionally, problems are provided for practice, such as determining segment lengths in parallelograms and understanding the relationships of their diagonals. This comprehensive approach is designed to reinforce key geometric concepts.

Understanding Parallelograms: Properties, Side Lengths, and Angle Measures
E N D
Presentation Transcript
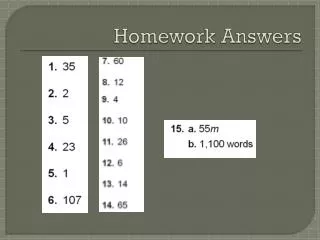
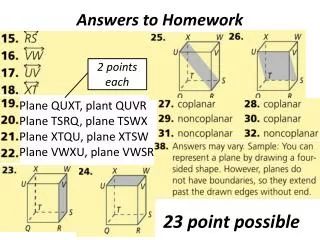
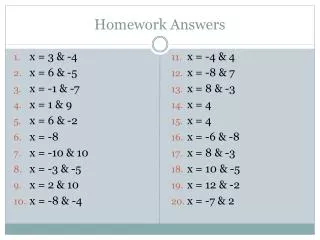
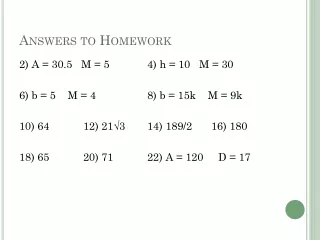
Homework Answers 8. Yes, pentagon • No, not formed by segments • Yes, 10-gon(Decagon) • 3 • 71° • 115° • 75° • 75 19. 20 • 44 • 8, octagon 22. Answers Vary • MP, MQ, MR, MS, MT • 6, hexagon • 8, octagon • 5, pentagon • 17, 17-gon
If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then its opposite sides are congruent.
Example 1 Find Side Lengths of Parallelograms FGHJ is a parallelogram. Find JH and FJ.
Checkpoint Find Side Lengths of Parallelograms 1. ABCD is a parallelogram. Find AB and AD.
If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then its opposite angles are congruent. If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then its consecutive angles are supplementary.
Example 2 Find Angle Measures of Parallelograms PQRS is a parallelogram. Find the missing angle measures.
Checkpoint Find Angle Measures of Parallelograms ABCD is a parallelogram. Find the missing angle measures. 2. 3.
If a quadrilateral is a parallelogram, then its diagonals bisect each other.
Example 3 Find Segment Lengths TUVW is a parallelogram. Find TX.