Termites and Mantids: Fascinating Insects of the Cenozoic Era
240 likes | 270 Vues
Explore the intriguing world of termites and mantids, two unique insect species that have thrived since the Cenozoic era. Termites, with their complex caste system and remarkable ability to digest cellulose, play a vital role in ecosystems. Mantids, known for their raptorial legs and sexual cannibalism behavior, are fascinating predators. Uncover the different types of termites based on their diets and habitats, and learn about the distinctive features of mantids. Discover how these insects have evolved and adapted over millions of years, shaping the biodiversity of the modern world.

Termites and Mantids: Fascinating Insects of the Cenozoic Era
E N D
Presentation Transcript
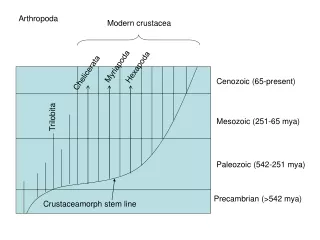
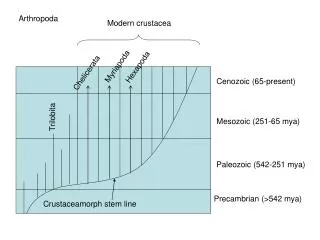
Arthropoda Modern crustacea Myriapoda Hexapoda Chelicerata Cenozoic (65-present) Trilobita Mesozoic (251-65 mya) Paleozoic (542-251 mya) Precambrian (>542 mya) Crustaceamorph stem line
Rupert et al. fig 21-23 Collembola Thysanura Ephemeroptera Odonata Neoptera “Apterygota” Pterygota Entognatha Insecta Hexapoda
Sternorrhyncha Mantodea Grylloblattaria Heteroptera Auchenorrhyncha Phasmida Anoplura Isoptera Holometabola Mallophaga Blattaria Zoraptera Psocoptera Orthoptera Thysanoptera Dermaptera Hemipteroids Plecoptera Neoptera
Zoraptera • Tropical • Live in rotting wood • Eat fungal hyphae, tiny arthropods • Poorly studied
Isoptera - termites Caste system within termite colonies Worker Soldier Queen Workers tend the colony, gather food Soldiers cannot feed themselves, they have a nozzle-shaped snout for exuding noxious chemicals; defend colony from ant attack. Queens add a set of ovaries with each molt → very high fecundity (1000’s/day); >1 Queen/colony; kings resemble large worker and mate repeatedly with queens
Termites • Several kinds of termites based on diet • Subterranean* (live up to 20 ft underground) • Soil-feeding • Drywood* • Dampwood • Grass-feeding * Types that infest and eat human buildings
Termites • All termites eat cellulose • Cellulose has high energy, but difficult to digest • Gut bacteria have cellulase • Gut protozoa have symbiotic bacteria in their guts • Some “higher” termites (subterranean) can produce cellulase, but they still also have a rich gut flora to aid in cellulose digestion
Mantodea – the mantids • Raptorial first legs (“praying”) (also preying!) • Mobile neck joint • 3 extra eye on top of head • Sexual cannibalism: females eats male during copulation to get food and enhance sexual performance (tonus and locomotion of abdominal activity)
Blattaria – the cockroaches • Aka blattodea • Have mobile neck joint • A few feed on wood and have endosymbiotic flagellates (like isopterans) • Fast runners!
Sternorrhyncha Mantodea Grylloblattaria Heteroptera Auchenorrhyncha Phasmida Anoplura Isoptera Holometabola Mallophaga Blattaria Zoraptera Psocoptera Orthoptera Thysanoptera Dermaptera Hemipteroids Plecoptera Neoptera
Hemipteroids • Have piercing, sucking mouthparts
Hemipteroids • In days of old… • O Hemiptera, O Homoptera • Current thinking: • O Heteroptera = true bugs • O Sternorryncha = aphids, scale insects • O Auchenorryncha = leaf hoppers, tree hoppers, plant hoppers, cicadas, spittlebugs • Many hemipteroids are important crop pests
Sternorryncha Both aphids and scale insects are important crop pests Both form mutualistic interactions with ants (produce honeydew in exchange for protection)
Psocoptera: bark lice, book lice • Live in humid crevices and feed on fungi (under bark, old musty books)
Other lice • O Anoplura – sucking lice of mammals • Often host-specific e.g. human crab louse, human head louse
Other lice • O Mallophaga – chewing lice • All non-anopluran lice (polyphyletic) • Mostly found on birds
Thysanoptera -thrips • Suctorial mouthparts • Common in flowers (serve as pollinators) • Vectors of disease on some crops • Fringed wings
Sternorrhyncha Mantodea Grylloblattaria Heteroptera Auchenorrhyncha Phasmida Anoplura Isoptera Holometabola Mallophaga Blattaria Zoraptera Psocoptera Orthoptera Thysanoptera Dermaptera Hemipteroids Plecoptera Neoptera
Holometabula • Development: larva to pupa to adult