Cell Division and Reproduction: The Process and Importance
200 likes | 222 Vues
Explore the process of cell division and its significance in growth, replacement, and repair. Discover the stages of mitosis and cytokinesis in the cell cycle.

Cell Division and Reproduction: The Process and Importance
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Chapter 8.1 Cell Division and Reproduction
Why do cells go through cell division? • To grow • Organisms grow by ADDING more cells • To replace dead cells • All cells will die so they need to be replaced • To replace damaged cells • Cells will be damaged by injury (cut)
Definition of Cell Division • Cell division is the process of one cell dividing into two identical daughter cells
DNA - Hereditary Material • DNA is stored in a eukaryotic cells nucleus • Plant cells • Animal cells
What is Chromatin? • Loose (stringy) DNA in a cells nucleus is called chromatin • DNA before cell division • DNA ‘hanging out’
Chromosome doubles • Chromatin condenses (shrinks up) and doubles just before cell division • This forms a chromosome (X). X X
What is a Chromosome? • A chromosome is a structure made up of DNA and protein in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell
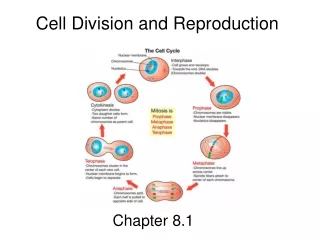
Cell Cycle • The cell cycle is the period of time from the beginning of one cell division to the beginning of the next. • The cell cycle has 3 parts: • Interphase See cycle on page 155 • Mitosis • Cytokinesis
1. Interphase • First part of the cell cycle • Time in between cell divisions • Cell is on vacation • Longest phase. Most time is spent in interphase • At end, chromatin (stringy) doubles into a chromosome (X)
Mitosis • Second part of the cell cycle • Makes 2 new identical nuclei • Has 4 steps: • Prophase • Metaphase • Anaphase • Telophase
2. Prophase • First step of mitosis • Chromatin in nucleus coils into chromosomes (X’s) • Nuclear membrane begins to disappear
3. Metaphase • Second step of mitosis • Chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell • Spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes
4. Anaphase • Third step of mitosis • Chromosomes separate and begin to move to opposite ends of the cell
5. Telophase • Final step of mitosis • Two new nuclei form around the separated chromosomes • Chromosomes unwind to form chromatin • Mitosis ends
6. Cytokinesis • Final part of the cell cycle • Makes 2 new identical daughter cells • Shortest phase • END of the cell cycle
Cell Cycle • Interphase • Prophase • Metaphase Mitosis • Anaphase • Telophase • Cytokinesis
Cell Cycle Mnemonic • Write a mnemonic for cell division • (Ex. King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk.) • I • P • M Add a COLORED • A picture • T • C
Cell Cycle Mnemonic • I • Played • Music • At • The • Concert