Beyond Our Solar System
840 likes | 1.02k Vues
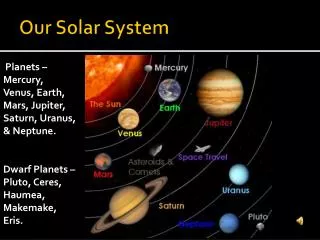
Beyond Our Solar System. Ch. 25. star : a body of gases that gives off a tremendous amount of radiant energy in the form of light and heat. Star Groups. constellations : a group of stars that form a pattern in the sky (88 different ones). Orion. Ursa Minor. Ursa Major.

Beyond Our Solar System
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Beyond OurSolar System Ch. 25
star: a body of gases that gives off a tremendous amount of radiant energy in the form of light and heat
Star Groups • constellations: a group of stars that form a pattern in the sky (88 different ones)
Ursa Minor Ursa Major
Composition and Temperature • stars differ in size, density, mass, and composition
color of a star depends on its surface temperature • hot stars areblue(average surface temperature 35,000 K) • cool stars arered(average surface temperature 3,000 K) • our sun isyellow(average surface temperature 5,500 K)
Parallax • the slight shifting of the apparent position of a star due to the orbital motion of Earth. • the nearest stars have the largest parallax angles, while those of distant stars are too small to measure.
Original Photo Photo taken 6 months later
Distance to Stars • light-year: the distance light can travel in one year (9.5 trillion km) • it takes 8 minutes for the sun’s light to reach Earth • closest other star- Alpha Centauri (4.3 l.y.a)
Motion • actual motion: must be measured only with a telescope • apparent motion: motion due to the Earth’s movement
Stellar Magnitudes • apparent magnitude: how bright a star appears from Earth- the lower the number, the brighter the object • absolute magnitude: how bright a star really is
Distance, Apparent Magnitude, and Absolute Magnitude of Some Stars
Electromagnetic Radiation The Study of Light Electromagnetic radiation includes gamma rays, X-rays, ultraviolet light, visible light, infrared radiation, microwaves, and radio waves. The electromagnetic spectrum is the arrangement of electromagnetic radiation according to wavelength.
a spectroscope is used to measure different compositions and temperatures • separates light into different colors • Hydrogen and Helium are most abundant elements in stars
spectrum of a star tells astronomers about its motion Sun Spectrum
Doppler effect: apparent shift in the wavelength of light emitted by a light source moving toward or away from the observer In astronomy, the Doppler effect is used to determine whether a star or other body in space is moving away from or toward Earth.
blue shift: light waves appear to have shorter wavelengths as the star movestowardthe Earth (spectrum shifted towardblueend) • red shift: light waves appear to have longer wavelengths as the star movesaway fromthe Earth (spectrum shifted towardredend)
Arefracting telescopeis a telescope thatuses a lens to bend or refract light.
Areflecting telescopeis a telescope that reflects light off a concave mirror, focusing the image in front of the mirror.
Detecting Invisible Radiation Tools for Studying Space Radio Telescopes • A radio telescope is a telescope designed to make observations in radio wavelengths. • A radio telescope focuses the incoming radio waves on an antenna, which, just like a radio antenna, absorbs and transmits these waves to an amplifier.
Space Telescopes 24.2 Tools for Studying Space Space telescopes orbit above Earth’s atmosphere and thus produce clearer images than Earth-based telescopes. Hubble Space Telescope • The first space telescope, built by NASA, was the Hubble Space Telescope. Hubble was put into orbit around Earth in April 1990.
Space Telescopes 24.2 Tools for Studying Space Other Space Telescopes • To study X-rays, NASA uses the Chandra X-Ray Observatory. This space telescope was launched in 1999. • Another space telescope, the Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory, was used to study both visible light and gamma rays. • In 2011, NASA plans to launch the James Webb Space Telescope to study infrared radiation.
protostar: shrinking, spinning, glowing nebula (temperature rises)
main sequence star: longest stage of life cycle- nuclear fusion releases energy
red giant: very large, cool bright stars- starts when hydrogen is used up- star cools and outer layers expand- size is 10x’s bigger than our sun- this is next stage of our sun!